Table of Contents
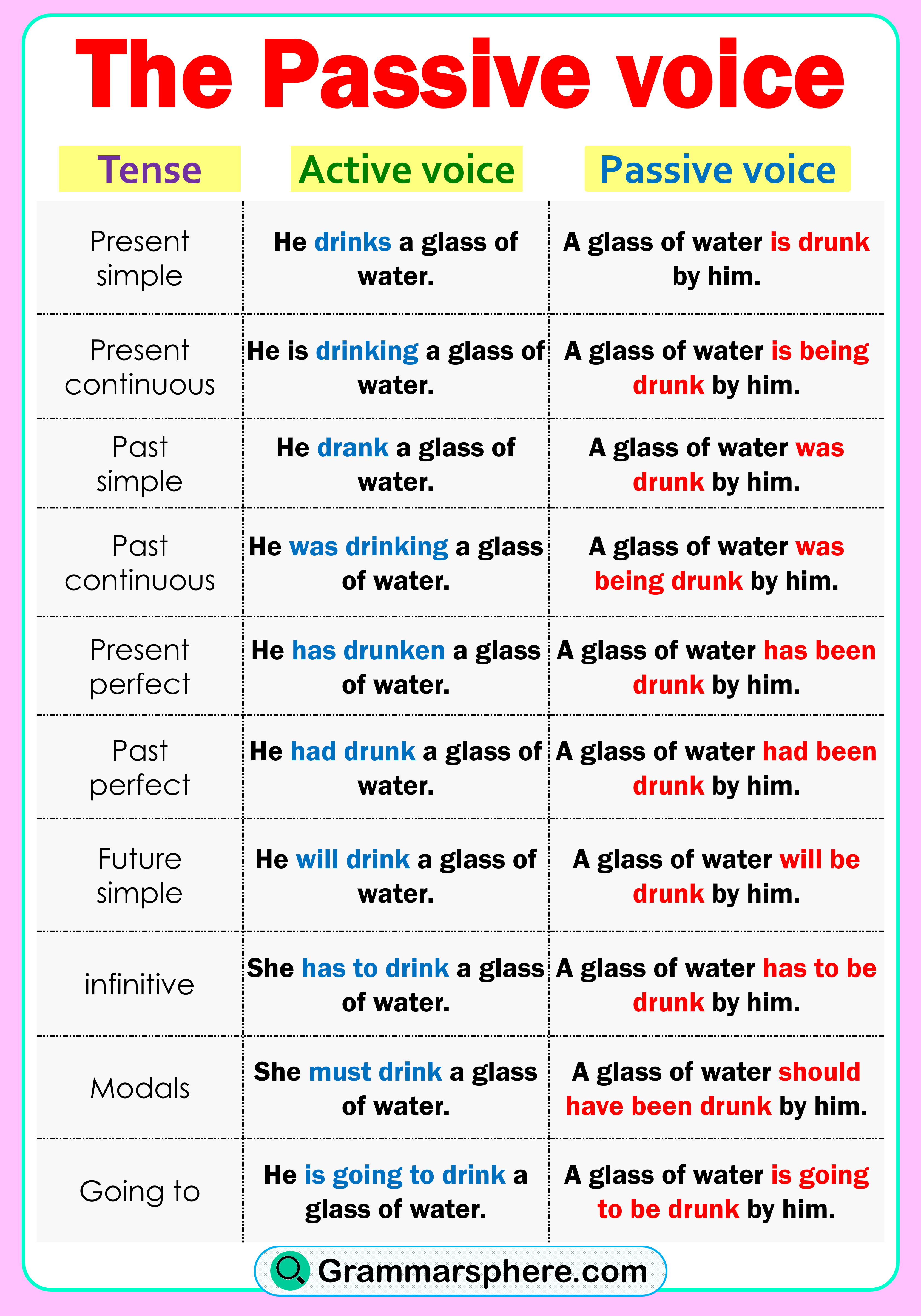
Active voice and passive voice are important parts of English grammar. Active voice focuses on the person or thing doing the action, while passive voice focuses on the action itself. Knowing how and when to use each type makes your writing clearer.
In this post, we’ll explain the difference between active and passive voice, with examples and simple tips to help you use them correctly and confidently in your writing.
What is Active Voice?
The formula is:
Subject + Verb + Object
The dog (subject) chased (verb) the ball (object).
In this case, it’s clear who is doing the action (the dog), making the sentence straightforward and easy to understand.
What is Passive Voice?
The formula is:
Object + Form of “to be” + Past Participle + (by Subject)
The ball (object) was chased (past participle) by the dog (subject).
In passive voice, the emphasis is on the ball rather than the dog.
Usage Of Active and Passive Voice
Active Voice:
In active voice, the subject performs the action. This style makes sentences direct, lively, and easy to understand. Active voice is often preferred in everyday writing, as it creates a stronger connection between the subject and the action.
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
(Here, the teacher is the subject actively doing the explaining.)
- She finished the project on time.
(In this sentence, she is the one actively completing the project.)
Passive Voice:
In passive voice, the focus is on the action or the object receiving the action, rather than the person or thing performing it. Passive voice is useful when the subject is unknown, less important, or when the emphasis is on the action itself.
- The lesson was explained clearly by the teacher.
(Here, the emphasis is on the lesson being explained, not on who explained it.)
- The project was finished on time.
(The focus is on the project being completed, rather than who completed it.)
Active Voice vs Passive Voice
Active Voice: Focuses on the subject doing the action.
- The chef cooked the meal.
Passive Voice: Focuses on the action being done to the object.
- The meal was cooked by the chef.
♦ Note: In many cases, active voice is preferred for clarity. However, passive voice is useful in scientific writing or formal contexts where the action is more important than the subject.
Examples In Sentences:
Active Voice:
- The teacher explains the lesson.”
- John fixed the car.
Passive Voice:
- The lesson was explained by the teacher.
- The car was fixed by John.
Notice how the emphasis shifts depending on whether the sentence is active or passive.
Rules for Using Active and Passive Voice
Active Voice
In active voice, the subject of the sentence performs the action. This construction is typically more direct and engaging. Here are some rules and examples:
Subject-Verb-Object Structure: Most sentences in active voice follow this structure.
- The dog Chased the cat.
The dog (subject)
chased (verb)
the cat (object).
In this case, the dog is performing the action of chasing.
Use in Everyday Conversation:
Active voice is commonly used in daily communication because it makes sentences more lively.
- My sister is studying math.
My sister (subject)
is studying (verb)
math (object).
This construction keeps the focus on my sister, who is performing the action of studying.
Clarity in Instructions:
When giving instructions or directions, active voice provides clarity.
- Please Turn off the lights.
Please turn off (verb)
the lights (object).
Here, the action is clear, and the sentence directs someone to perform a specific task.
Passive Voice
In passive voice, the subject receives the action, often leading to a focus on the action itself rather than the doer. Understanding when to use passive voice is essential, especially in formal writing. Here are some rules and examples:
Subject-Verb-Complement Structure:
Passive voice often changes the structure to emphasize the action or the receiver.
- The cake was baked by my mother.
The cake (subject)
was baked (verb)
by my mother (doer).
This sentence highlights the cake as the focus, rather than who baked it.
Use When the Doer is Unknown: When the identity of the doer is unknown or irrelevant, passive voice is appropriate.
- The window was broken.
The window (subject)
was broken (verb).
In this case, it doesn’t matter who broke the window; the focus is on the damage itself.
Emphasizing Results in Formal Writing:
Passive voice is often preferred in academic or professional contexts where the action or result is more important than the actor.
- The results of the study were published in a journal .
The results of the study (subject)
were published (verb)
in a journal (by whom is not specified).
Here, the emphasis is on the results, not on the researchers.
Politeness or Indirectness:
Passive voice can make statements sound more polite or less direct.
Active Voice:
You didn’t complete the report on time.
Passive Voice:
The report wasn’t completed on time.”
The passive voice here makes the statement less direct and more polite.
Common Mistakes
When using active and passive voice, beginners often encounter a few common mistakes that can lead to confusion. Understanding these errors can help you write more clearly and effectively.
One common mistake is overusing passive voice in situations where active voice would be more appropriate. This can make your writing less engaging and harder to follow.
✓ The teacher grades the assignments.
✗ The assignments are graded by the teacher.
In the first example, the subject (the teacher) is doing the action, making the sentence clear and direct. The second example, while correct, feels less dynamic and can be unnecessarily complex.
Another mistake is confusing the focus of the sentence. In passive constructions, the doer of the action can sometimes be left out, leading to confusion. It’s essential to be clear about who is performing the action.
✓ The dog barked at the stranger.
✗ The stranger was barked at by the dog.
In the first example, the focus is on the dog, making it clear who is taking action. The second example sounds awkward and shifts the focus away from the dog.
A third common mistake is using the wrong verb form in passive sentences. The passive voice requires the correct form of the verb “to be” along with the past participle of the main verb.
✓ The project was completed on time.
✗ The project is completed on time.
In the first sentence, the past participle “completed” is correctly used with the past form of “to be,” creating a proper passive structure. The second example incorrectly uses “is,” which can confuse the time aspect of the sentence.
Finally, beginners often neglect to adjust tense consistency when switching between active and passive voice. Maintaining the same tense helps ensure clarity.
✓ The committee approved the proposal yesterday.
✗ The proposal was approved by the committee yesterday.
Both examples are correct, but if you change tenses incorrectly, such as saying “The proposal is approved by the committee yesterday,” it becomes unclear and inconsistent.
By avoiding these common mistakes and practicing the appropriate use of active and passive voice, you can improve your writing clarity and effectiveness.
Example Sentences with Active Voice and Passive
Active Voice Examples
- The chef prepared a delicious meal.
- The students completed their homework on time.
- She painted the walls yesterday.
- They cleaned the house thoroughly.
- The company launched a new product last month.
Passive Voice Examples
- A delicious meal was prepared by the chef.
- The homework was completed on time by the students.
- The walls were painted yesterday by her.
- The house was cleaned thoroughly by them.
- A new product was launched last month by the company.
Change of Pronouns:
| I | Me |
| She | Her |
| He | Him |
| We | Us |
| It | It |
| They | Them |
How to change passive voice to active voice
To change a sentence from passive voice to active voice, follow these steps:
Identify the subject, verb, and object in the passive sentence.
Move the subject (the one performing the action) to the beginning of the sentence.
Rewrite the verb to match the new active structure.
Examples
- Passive: The report was written by Sarah.
Step 1: Identify the subject (Sarah),
verb (was written),
and object (the report).
Step 2: Move Sarah to the beginning of the sentence.
- Step 3: Rewrite the sentence: Sarah wrote the report.
More Examples:
- Passive: The cake was baked by John.
Active: John baked the cake. - Passive: The song was sung by the choir.
Active: The choir sang the song.
FAQS about Active and Passive Voice
1. What is the difference between active and passive voice?
In passive voice, the subject receives the action (e.g., The mouse was chased by the cat).
2. When should I use the passive voice?
The doer of the action is unknown (The window was broken).
The focus is on the action or the receiver (The project was completed on time).
You want to sound formal or impersonal (Mistakes were made).
3. How do I change a sentence from active to passive voice?
Identify the object in the active sentence.
Make it the subject in the passive sentence.
Use the correct form of “to be” + past participle of the verb.
Add “by” + the original subject if necessary.
Example:
Active: She writes a letter.
Passive: A letter is written by her.
4. Are there tenses that cannot be changed into passive voice?
Intransitive verbs (verbs without an object) (He sleeps. cannot be passive).
Present perfect continuous (He has been writing letters).
5. How can I identify a passive sentence?
You May Also Like






Leave a Comment