Table of Contents
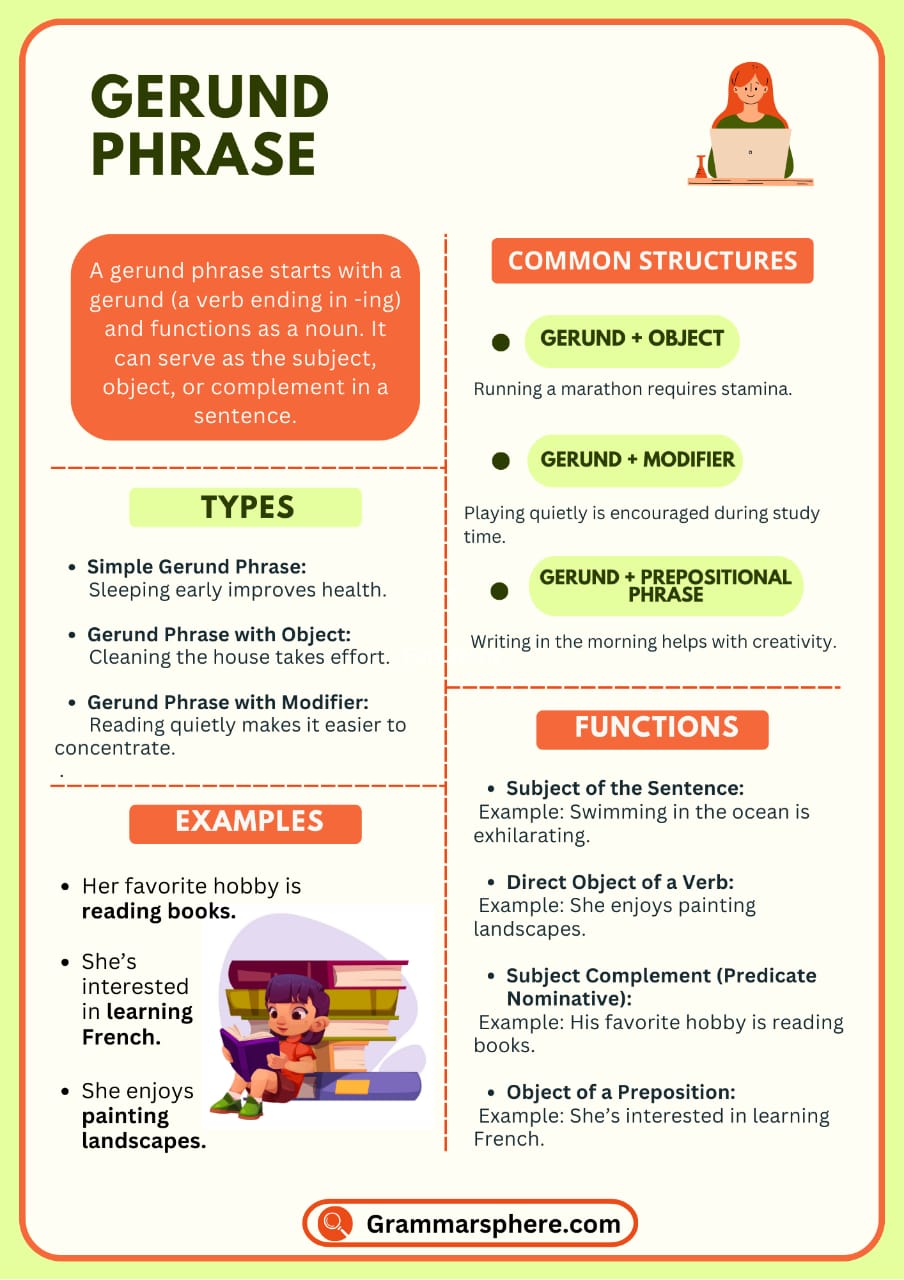
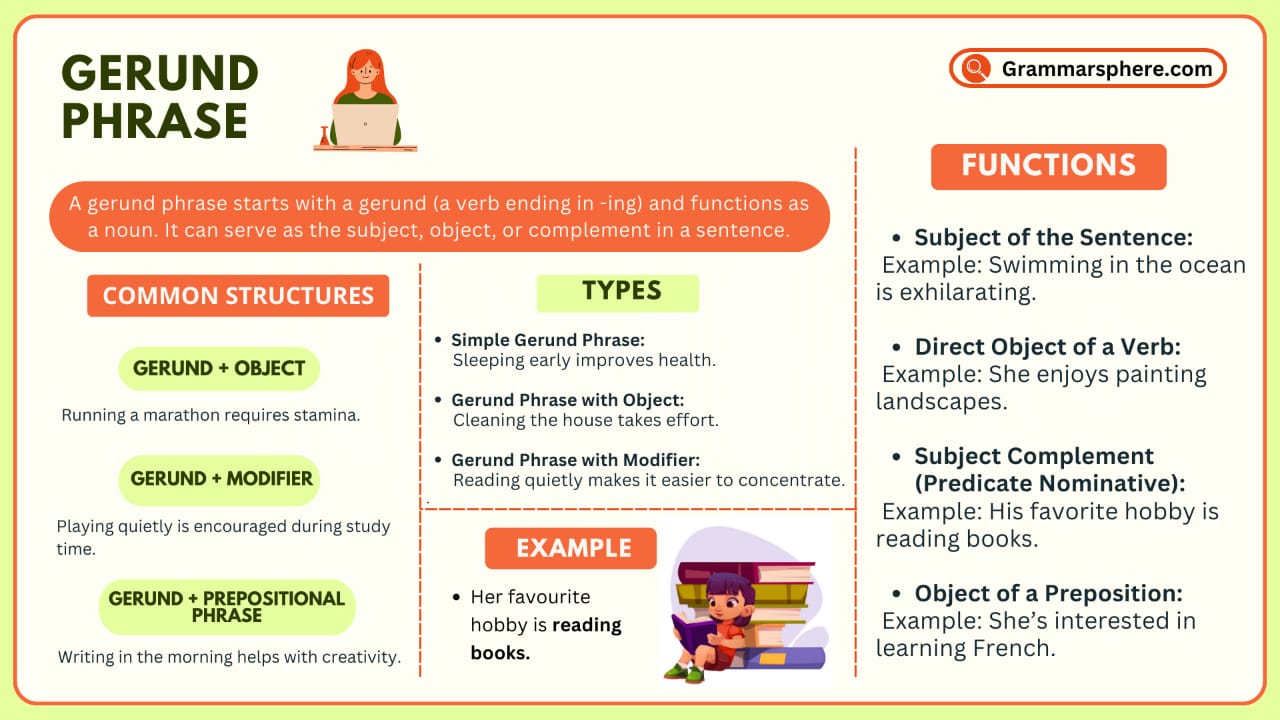
A gerund phrase consists of a gerund (a verb ending in -ing) along with its modifiers or objects, functioning as a noun. It can serve as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence. Understanding gerund phrases improves sentence clarity and structure.
What is a Gerund Phrase?
A gerund phrase begins with a gerund (a verb ending in -ing used as a noun) and includes any modifiers or objects. The entire phrase functions as a noun in a sentence.
Examples:
- Swimming in the ocean is fun. (Subject)
- She loves reading books. (Object)
- His hobby is writing stories. (Complement)
Gerund Phrases vs Participle Phrases
| Feature | Gerund Phrase | Participle Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Starts with a gerund (-ing form used as a noun) | Starts with a participle (-ing or -ed form used as an adjective) |
| Function in Sentence | Acts as a noun (subject, object, or complement) | Acts as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun |
| Example | Walking in the park is refreshing. (Subject) | The boy, running fast, won the race. (Describes the boy) |
| = | She enjoys cooking new recipes. (Object) | Exhausted from work, she went to bed early. (Describes “she”) |
Common Mistakes: Gerund Phrases vs. Participle Phrases
Many learners confuse gerund phrases with participle phrases because both start with -ing verbs. However, they serve different purposes:
- A gerund phrase acts as a noun (subject, object, or complement).
- A participle phrase acts as an adjective, describing a noun or pronoun.
1. Using a Participle Instead of a Gerund
✗ Running in the morning, she enjoys the fresh air. (Incorrect if intending a gerund phrase)
✓ Running in the morning improves health. (Correct gerund phrase as subject)
2. Using a Gerund Instead of a Participle
✗ She saw a singing in the choir girl. (Incorrect)
✓ She saw a girl singing in the choir. (Correct participle phrase describing girl)
How Gerund Phrases Function in a Sentence
A gerund phrase functions as a noun in a sentence. It can serve as a subject, object, or complement. Since it begins with a gerund (a verb ending in -ing), the entire phrase takes on the role of a noun.
1. As a Subject
- Swimming in the morning improves your health.
(Swimming in the morning is the subject of the sentence.)
2. As an Object
- He enjoys playing football with friends.
(Playing football with friends is the object of the verb enjoys.)
3. As a Complement
- Her hobby is painting beautiful landscapes.
(Painting beautiful landscapes completes the meaning of the verb is.)
Parts of a Gerund Phrase
A gerund phrase is made up of a gerund (the base of the phrase) and additional parts that modify or complete its meaning. These parts work together to form a meaningful unit acting as a noun in a sentence.
1. Gerund
The -ing form of a verb that acts as a noun.
- Running helps keep you fit.
2. Object
A noun or pronoun that receives the action of the gerund.
- He enjoys reading novels. (Novels is the object of reading.)
3. Modifiers
Words that describe or provide more detail about the gerund or object.
- Walking quickly is good exercise. (Quickly modifies walking.)
A phrase that adds more information to the gerund.
- She loves dancing at parties. (At parties is a prepositional phrase modifying dancing.)
When to Use a Gerund Phrase?
A gerund phrase is used when you need to express an action as a noun in a sentence. Understanding when to use a gerund phrase vs. an infinitive helps in making writing more natural and fluent.
1. Gerund Phrases vs. Infinitives
Gerund phrases are often used after verbs that express liking, disliking, or continuation.
✓ I enjoy swimming in the lake.
✗ I enjoy to swim in the lake.
Infinitives are more common after verbs that express decisions, intentions, or desires.
✓ She decided to swim in the lake.
✗ She decided swimming in the lake.
- I stopped smoking. (Stopped the habit of smoking)
- I stopped to smoke. (Paused another activity to start smoking)
2. Using Gerund Phrases for Better Sentence Flow
Gerund phrases make sentences smoother by avoiding awkward or overly direct constructions.
Instead of It is fun to swim in the lake,
✓ Swimming in the lake is fun. (More natural and direct)
Instead of To learn English is important,
✓ Learning English is important. (Flows better and sounds more natural)
Using gerund phrases reduces redundancy and creates a more fluid sentence structure.
Difference Between Gerund and Gerund Phrase
| Aspect | Gerund | Gerund Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A verb ending in -ing that functions as a noun | A gerund plus its modifiers or objects, acting as a noun |
| Structure | Only the -ing form of the verb | Includes the gerund + extra words (modifiers, objects) |
| Example | Swimming is fun. (“Swimming” is the subject) | Swimming in the pool is fun. (The whole phrase is the subject) |
| Focus | Focuses only on the action as a noun | Adds details or context to the action being described |
Examples of Gerund Phrases in Sentences
- Swimming in the ocean is a thrilling experience.
- She enjoys reading books on rainy afternoons.
- Walking through the park helps me relax.
- Learning a new language can open many opportunities.
- Baking cakes for special occasions is her favorite hobby.
- They avoided arguing during the meeting.
- Watching movies late at night has become a habit.
- His dream is traveling around the world.
- The coach suggested practicing harder before the match.
- Writing essays for school projects takes a lot of time.
Importance of Gerund Phrases
Gerund phrases make your sentences more interesting by turning actions into nouns. They can be used as the subject, object, or complement, helping you say more with fewer words. Phrases like “Writing stories” or “Traveling abroad” sound smoother and clearer, making your English more natural and fluent.
ty, clarity, and variety, allowing you to express actions and ideas in a more detailed and natural way.
Common Mistakes with Gerund Phrases
Many learners make mistakes when using gerund phrases due to confusion with other structures. Below are common errors and how to fix them.
1. Using a Gerund Instead of an Infinitive
✗ She wants reading a book.
✓ She wants to read a book.
2. Confusing Gerund Phrases with Participle Phrases
✗ Running in the morning, she enjoys the fresh air.
✓ Running in the morning improves health.
3. Wrong Preposition After a Gerund
✗ He is good in playing football.
✓ He is good at playing football.
4. Forgetting the Object or Modifier
✗ She enjoys. (Incomplete)
✓ She enjoys playing the piano. (Complete)
5. Placing a Comma Incorrectly
✗ Before sleeping, I always brush my teeth.
✗ I always brush my teeth, before sleeping.
Frequently Asked Questions on Gerund Phrases
Q1: What is a gerund phrase?
A gerund phrase consists of a gerund (a verb ending in -ing that acts as a noun) along with its modifiers or objects. It functions as a noun in a sentence.
Q2: How do gerund phrases function in sentences?
Gerund phrases can function as subjects, objects, or complements.
For example:
Subject: Swimming in the lake is refreshing.
Object: I enjoy reading mystery novels.
Q3: What is the difference between a gerund phrase and a participial phrase?
A gerund phrase acts as a noun, while a participial phrase acts as an adjective describing a noun.
Gerund Phrase: Running in the park is fun. (noun)
Participial Phrase: The girl running in the park is my sister. (adjective)
Q4: How can I quickly identify a gerund?
Look for a verb ending in -ing and check if it is used as a noun.
For example:
Running is healthy. (Gerund as a subject)
Q5: How does a gerund function in a sentence?
A gerund can function as a subject, object, or complement:
Subject: Swimming is fun.
Object: She loves dancing.
Complement: His favorite hobby is fishing.
Q6: How can I identify a gerund in a sentence?
Look for a word ending in -ing that acts as a noun. If it names an activity or action, it is a gerund.
Example: Jogging is my favorite exercise. (Here, jogging is the gerund acting as the subject.)
You May Also Like


Leave a Comment