Table of Contents
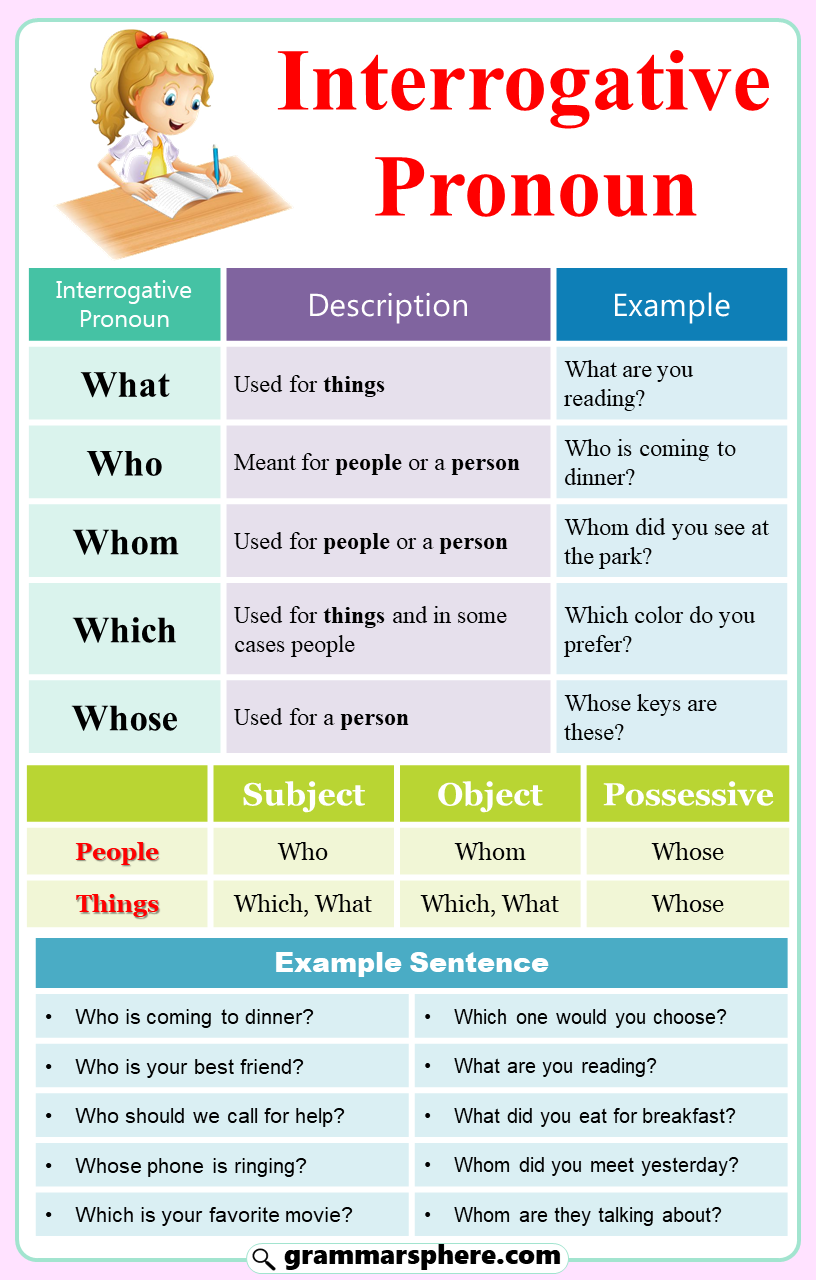
Interrogative pronouns are essential in English for asking clear and direct questions. Words like who, what, which, whom, and whose help us gather specific information by referring to people, objects, or choices.
These pronouns are important in forming questions that lead to better communication and understanding. In this post we will discuss what interrogative pronouns are, how to use them correctly in sentences, and provide helpful examples.
What Are Interrogative Pronouns?
Interrogative pronouns are words used to ask questions about people, things, or choices. They include who, whom, whose, what, and which. These pronouns help focus the question on a specific person or object.
Example Sentences:
Who is your best friend?
Whose phone is this?
What time is the meeting?
Which dress do you like?
Whom did you speak to?
Use of Interrogative Pronoun
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions and gather more information.
Who is used to ask about the person performing an action.
- Who is coming to the party?
Here, who is the subject of the verb is coming.
What is used to ask about something?
- What is your favorite color?
Here, what asks for information about your favorite color?
Which is used to ask about a choice between two things.
- Which dress do you like, the red one or the blue one?
Here, it asks the listener to choose from specific options.
Whom is used to ask about the person affected by an action?
- Whom did you invite to the party?
Here, whom is the object of the verb invite
Whose is used to ask about possession.
- Whose book is this?
Here, whose is asking who owns the book.
By using interrogative pronouns, we can ask questions and get more information about something or someone.
Interrogative Pronouns Examples
- Who is your favorite author?
- What time does the meeting start?
- Whom did you see at the concert?
- Whose jacket is lying on the table?
- Which movie do you want to watch tonight?
- Who will be leading the presentation?
- What is the capital of France?
- Whom should I contact for more information?
- Whose turn is it to do the dishes?
Interrogative Pronouns vs. Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative pronouns and interrogative adjectives help ask questions, but their roles are quite different.
Interrogative pronouns replace a noun in a question. They stand alone without needing a noun right after them. These pronouns ask about a person, thing, or information.
- Who: asks about a person (subject)
- Whom: asks about a person (object)
- What: asks about a thing or information
- Which: asks about a choice from a set
- Whose: asks about possession
Examples:
- Who is your teacher?
Who replaces the noun, asking about the identity of the teacher.
- What is your favorite color?
What stands alone, asking about the color.
- Which is your bag?
Which is used to ask for a choice, replacing the noun bag.
Interrogative Adjectives:
Interrogative adjectives are used before a noun to modify it. They don’t replace the noun but describe it in a question. These adjectives ask about the characteristics of the noun they modify.
- What: asks about the type or kind of something
- Which: asks about a specific choice
- Whose: asks about possession
Examples:
- What book are you reading?
What modifies the noun book, asking about the type or title of the book?
- Which dress should I wear?
Which is modifying dress, asking for a choice between dresses.
- Whose phone is this?
Whose modifies the noun phone, asking about the owner.
Why Interrogative Pronouns Are Important
Interrogative pronouns are important because they help us ask precise and direct questions, which improves clarity in communication. By using these pronouns, we can specify what or whom we are asking about, which is crucial for gathering accurate information.
Examples:
- Who is responsible for this project? (asking about a person)
- What do you need? (asking about an object or idea)
- Whose book is this? (asking about ownership)
Who vs. Whom
The difference between who and whom can be tricky, but it’s important to understand for proper English grammar. Both words are used to refer to people, but they serve different roles in a sentence.
Who:
Who is used as the subject of a sentence or clause? It is the person acting.
- Who is coming to the party?
Here, who is the subject—who is doing the action of coming?
- Who called me last night?
Who is the one doing the calling.
Whom:
Whom is used as the object of a verb or preposition? It refers to the person who is receiving the action.
- Whom did you invite to the party?
Here, whom is the object of the verb invite—the person being invited.
- To whom are you speaking?
Here, whom is the object of the preposition to—the person you are speaking to.
Tip: If you can replace the word with he or she, use who. If you can replace it with him or her, use whom.
What vs. Which
The difference between what and which can also be subtle, but it’s helpful when asking specific or general questions.
What:
What is used when asking for general information or when there is a broad range of possible answers? It is not limited to a particular set of options.
- What do you want for lunch?
There is a wide range of possibilities for what the person might want.
- What is your favorite color?
This question is asking for any color, not a specific set of colors.
Which:
Which is used when there is a specific set of options to choose from. It’s often used when you are choosing from a known or limited number of things.
- Which color do you prefer, red or blue?
Here, the choice is between two options, so which is used?
- Which book should I read next?
The question implies a set of books, like those on a shelf or in a list.
Tip: Use what when the range of options is open or unclear, and which when the options are more limited or defined.
Compound Interrogative Pronouns
Compound interrogative pronouns are formed by combining an interrogative pronoun with another word like ever, so ever, else, or that. These compound pronouns provide more specific or complex questions.
They are often used to ask about specific choices, times, or quantities, making them more detailed than standard interrogative pronouns.
- Whoever
- Whomever
- Whatever
- Whichever
- Whosoever
- Whatsoever
Whoever:
Refers to any person, without specifying exactly who.
- Whoever told you that is wrong. Anyone who told you this is wrong.
Whomever:
Refers to any person, but it is used as the object of a verb or preposition.
- I will give it to whomever needs it most. Anyone who needs it most will get it.
Whatever:
Refers to anything or everything, often used in questions to mean anything at all.
- Whatever you choose will be fine. (Anything you choose is acceptable.
Whichever:
Refers to a specific selection from a set of options.
- Whichever dress you pick, I will like it. (From the available dresses, anyone is fine.)
You May Also Like





Leave a Comment