Table of Contents
Many English learners struggle with using the present continuous tense correctly. When should you use “is,” “am,” or “are”? How do you form negative and question sentences? This blog post helps learn present continuous tense with clear rules and easy-to-understand explanations. You’ll discover its usage, structure, and common mistakes to avoid. Mastering this tense will improve your ability to describe actions happening right now.
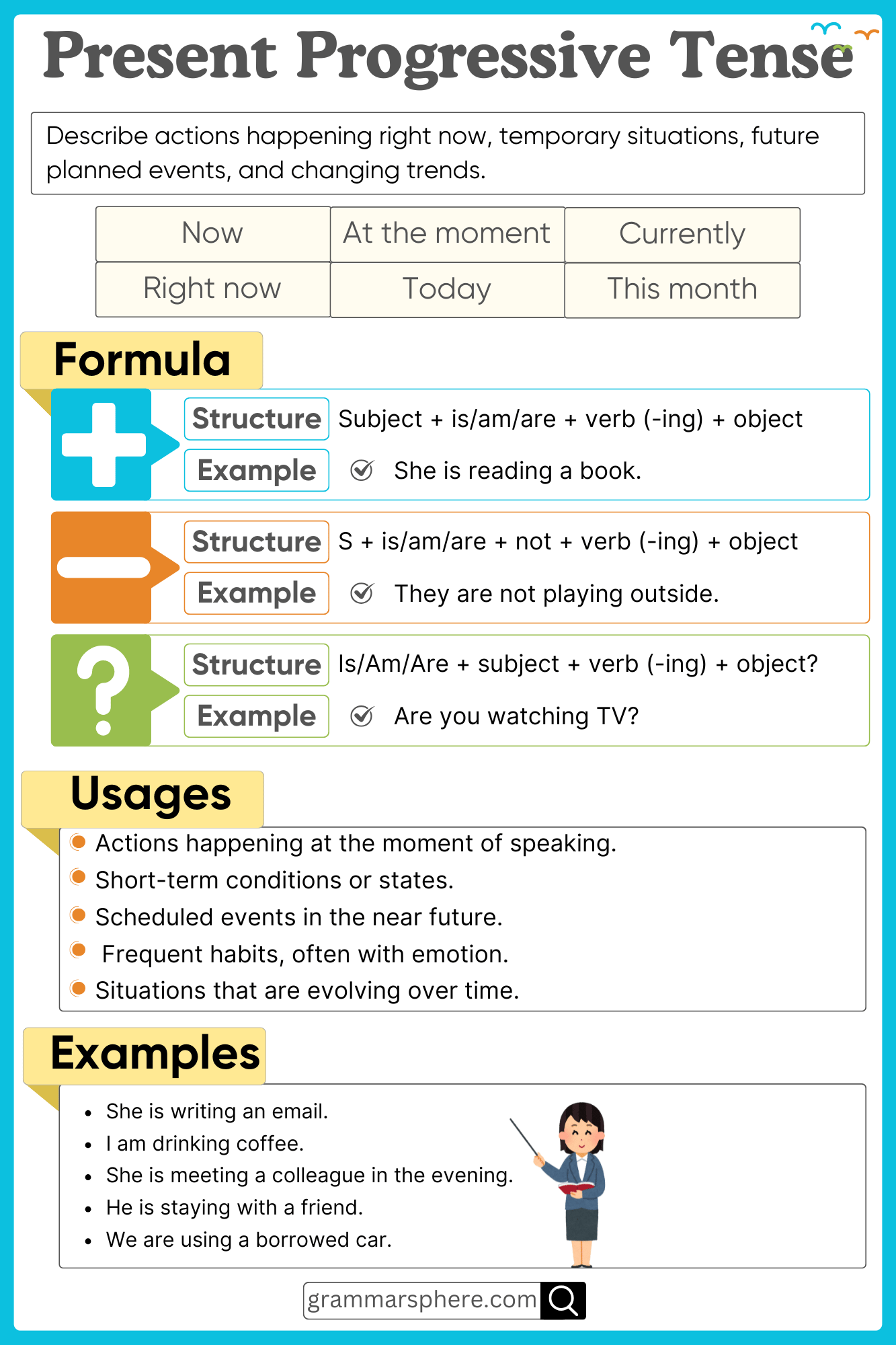
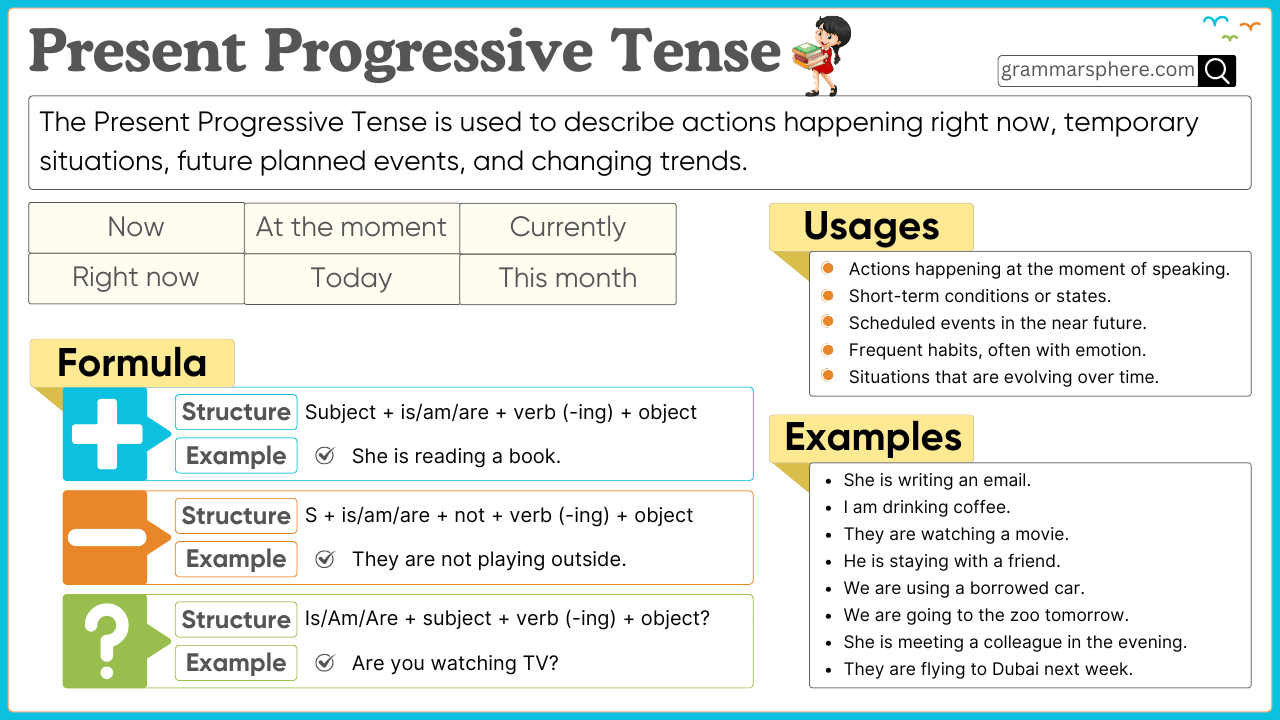
Definition of Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense describes actions happening right now or in progress at the moment of speaking. It is also used for future planned events. This tense is essential for expressing ongoing situations and temporary actions.
Structure of the Tense
The Present Continuous Tense is formed using: Subject + am/is/are + verb(-ing)
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha is reading a book.
- They are playing football.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + not + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha is not reading a book.
- They are not playing football.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Am/Is/Are + subject + verb(-ing) + object?
- Is Aisha reading a book?
- Are they playing football?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + am/is/are + subject + verb(-ing) + object?
- What is Aisha reading?
- Why are they playing football?
Subject-Verb Agreement
The helping verb changes depending on the subject:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| I | am |
| He/She/It | is |
| We/You/They | are |
Time Expressions
These words indicate when the action is happening:
- Now: I am cooking now.
- At the moment: He is studying at the moment.
- Currently: They are working currently.
Adverb Placement in the Present Continuous Tense
In the present continuous tense (is/am/are + verb-ing), adverbs are placed in specific positions based on their type.
1. Before the Main Verb (Common Placement)
Adverbs of frequency (always, often, sometimes) usually go before the main verb (verb+ing).
- She is always talking during meetings. ✅
- She always is talking during meetings. ❌
2. After the “Be” Verb (Alternative Placement)
Some adverbs (especially manner adverbs) can come after the auxiliary verb (is/am/are).
- He is quickly learning English.
- He is learning quickly.
3. At the End of the Sentence
Adverbs of manner, place, and time are often placed at the end.
- They are playing outside. (Place)
- I am studying hard. (Manner)
- She is working now. (Time)
4. At the Beginning for Emphasis
Adverbs of time can sometimes start a sentence for emphasis.
- Right now, they are preparing for the test.
Uses of the Present Continuous Tense
1. Actions Happening Now
Used for actions taking place at this moment. These actions are still in progress.
✅ Fatima is writing an email. (She has not finished writing yet.)
2. Temporary Situations
Describes situations that are not permanent and last for a short time.
✅ Ahmed is staying in a hotel this week. (His stay is temporary, not permanent.)
3. Future Plans
Used for fixed plans or arrangements in the near future.
✅ We are traveling to Turkey next month. (The plan is already decided.)
4. Repeated Actions (with ‘always’)
Expresses irritation or habits that happen frequently.
✅ He is always losing his keys! (This happens too often, and it’s frustrating.)
Present Continuous vs the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Here is the comparison between the Present Continuous Tense and the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in a table format:
| Feature | Present Continuous Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Describes an action happening right now or a temporary situation. | Describes an action that started in the past and is still continuing or has recently stopped with a result in the present. |
| Formula | Subject + is/am/are + Verb (-ing) + Object | Subject + has/have + been + Verb (-ing) + Object |
| Usage | 1. Action happening at the moment of speaking (Omar is talking on the phone right now). 2. Temporary situations (Fatima is staying with her aunt this week). | 1. Action that began in the past and is still continuing (Aisha has been reading this book for two hours). 2. Action that recently stopped but has an effect on the present (Ahmed has been running, so he is tired now). |
| Examples | “Hassan is watching a movie at the moment.” “We are learning Arabic this semester.” | “I have been studying since morning.” “She has been working at this company for five years.” |
Examples of the Present Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative Sentences:
- Ayesha is reading a storybook.
- The birds are chirping in the trees.
- Ahmed is writing a letter to his friend.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully.
- They are watching a football match.
Negative Sentences:
- Fatima is not eating her lunch.
- The boys are not playing in the park.
- He is not doing his homework.
- We are not going to the market today.
- The cat is not sitting on the sofa.
Interrogative Sentences:
- Is Hina cooking dinner?
- Are the students studying for the exam?
- Is your father coming home early?
- Are they going to the mosque?
- Is he watching TV right now?
Common Mistakes with the Tense
- He play football now. ❌
- He is playing football now. ✅
- We are go to the market. ❌
- We are going to the market. ✅
- She is work in the office. ❌
- She is working in the office. ✅
FAQs
When do we use the Present Continuous Tense?
We use it for actions happening now, temporary situations, future plans, and repeated actions with ‘always’.
What is the difference between Present Continuous and Present Simple?
Present Continuous is for ongoing actions, while Present Simple is for habits and facts.
Can we use stative verbs in Present Continuous?
No, verbs like know, believe, love, hate usually don’t take -ing.
Read More





Leave a Comment