Table of Contents
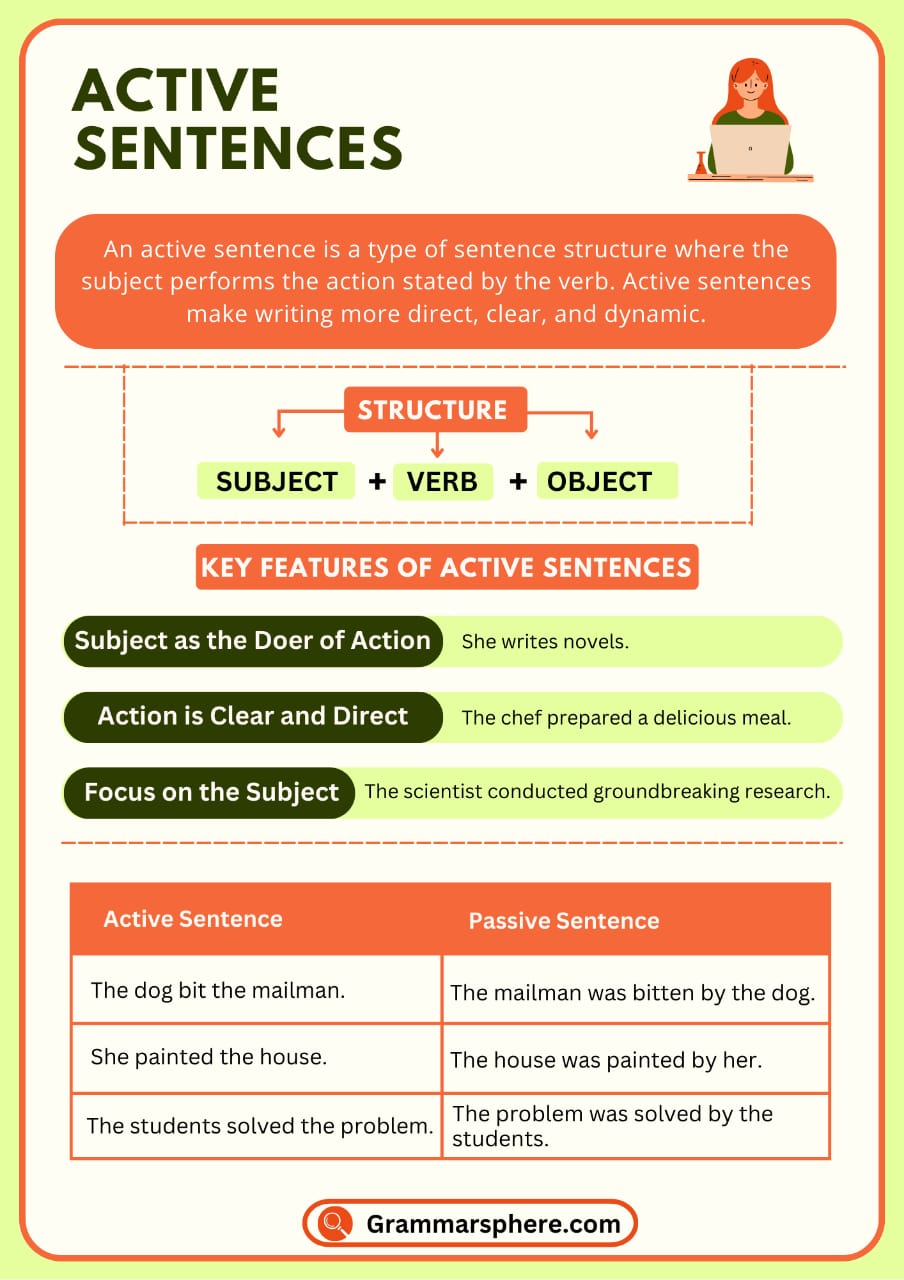
Active sentences have a subject that performs the verb’s action, ensuring clarity and directness. They follow a subject-verb-object structure, making writing stronger and more engaging. Common in speech and writing, active sentences improve readability and effectiveness.
What Is an Active Sentence?
An active sentence is a sentence where the subject performs the action described by the verb. This structure keeps the sentence clear, direct, and engaging.
Example Sentences:
- The cat chased the mouse.
- She wrote a letter.
- They built a new house.
In these examples, the subjects (cat, she, they)
Structure of Active Sentences
Active sentences generally follow the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) pattern:
Subject + Verb + Object
Example:
- John (Subject) kicks (Verb) the ball (Object).
Types of Active Sentences Based on Tense
Active sentences can be written in different tenses. Below are examples of how they change with different tenses:
| Tense | Active Sentence |
|---|---|
| Present Simple | She writes a letter. |
| Present Continuous | She is writing a letter. |
| Past Simple | She wrote a letter. |
| Past Continuous | She was writing a letter. |
| Future Simple | She will write a letter. |
| Future Continuous | She will be writing a letter. |
Why Active Sentences Are Important
1. Clarity and Simplicity
Active sentences make it easy to identify the subject and the action, making communication clearer.
- Active: The teacher explained the lesson.
- Passive: The lesson was explained by the teacher.
The active sentence is more straightforward.
2. Engagement and Impact
Active sentences create a more dynamic and engaging tone.
- Active: Sarah painted a beautiful portrait.
- Passive: A beautiful portrait was painted by Sarah.
3. Stronger Writing Style
Active sentences are concise and avoid unnecessary words, improving the flow of writing.
- Active: The athlete broke the record.
- Passive: The record was broken by the athlete.
Common Mistakes in Active Sentences
1. Overusing Weak Verbs
Avoid weak verbs like is, was, has been, which make sentences passive.
✗ The cake was baked by Sarah. (Passive)
✓ Sarah baked the cake. (Active)
2. Forgetting the Subject
A complete active sentence requires a clear subject performing the action.
✗ Ran to the store. (Who ran?)
✓ She ran to the store.
Converting Passive Sentences to Active Sentences
Converting passive sentences into active ones improves clarity and engagement. Follow these steps:
- Identify the subject, verb, and object in the passive sentence.
- Rearrange the sentence so that the subject appears first.
- Use a strong action verb to replace weak verbs like “was” or “been.”
Example Conversion:
- Passive: The book was read by Sarah.
- Active: Sarah read the book.
When to Prefer Active Sentences Over Passive Sentences
Active sentences are preferred when:
- The subject is more important than the action.
- You want to create a stronger and clearer message.
- Writing for conversational or engaging content.
However, passive sentences may be useful when:
- The doer of the action is unknown or unimportant (e.g., “A mistake was made.”)
- The focus is on the action itself rather than the subject.
Summary
- Active sentences focus on the subject performing the action.
- They follow a clear Subject-Verb-Object structure.
- They are direct, engaging, and concise.
- Active sentences improve writing clarity and impact.
- Converting passive to active makes writing stronger and more effective.
Examples of Active Sentences in Different Tenses
1. John eats an apple.
- This is an active sentence because the subject John) performs the action eats on the object an apple.
2. She is writing a letter.
- In this sentence, the subject She is actively performing the action writing on the object (a letter). The verb is in the present continuous tense.
3. The dog chased the cat.
- This active sentence shows the subject The dog doing the action chased to the object the cat.
4. They will build a new house.
- Here, the subject They actively performs the action will build on the object a new house. The verb is in the future tense.
5. The teacher explained the lesson.
- In this sentence, the subject The teacher actively performs the action explained to the object the lesson.
Active to Passive Sentences Table
| Active Sentence | Passive Sentence |
|---|---|
| John completed the project. | The project was completed by John. |
| The teacher praised the student. | The student was praised by the teacher. |
| She is cleaning the house. | The house is being cleaned by her. |
| They will deliver the package. | The package will be delivered by them. |
| The chef cooked a delicious meal. | A delicious meal was cooked by the chef. |
Example Sentences with Active Voice
- John drives a car every day.
- She wrote a letter to her friend.
- The chef prepared a delicious meal.
- They will build a new house next year.
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
- Tom kicks the ball with great force.
- Lisa is painting a beautiful picture.
- The dog chased the cat across the street.
- We watched an interesting movie last night.
- The company launched a new product this month.
FAQS about Active Sentences
1. What is an active sentence?
An active sentence is one in which the subject performs the action of the verb. It follows the structure Subject → Verb → Object and makes the message clear and direct.
Example: The cat chased the mouse.
2. How is an active sentence different from a passive sentence?
In an active sentence, the subject performs the action, while in a passive sentence, the subject receives the action.
Active: The chef cooked the meal.
Passive: The meal was cooked by the chef.
3. Why are active sentences important?
Active sentences improve clarity, make writing concise, and engage readers by emphasizing the subject’s actions. They are preferred in both academic and professional writing for their straightforwardness.
You May Also Like




Leave a Comment