Table of Contents
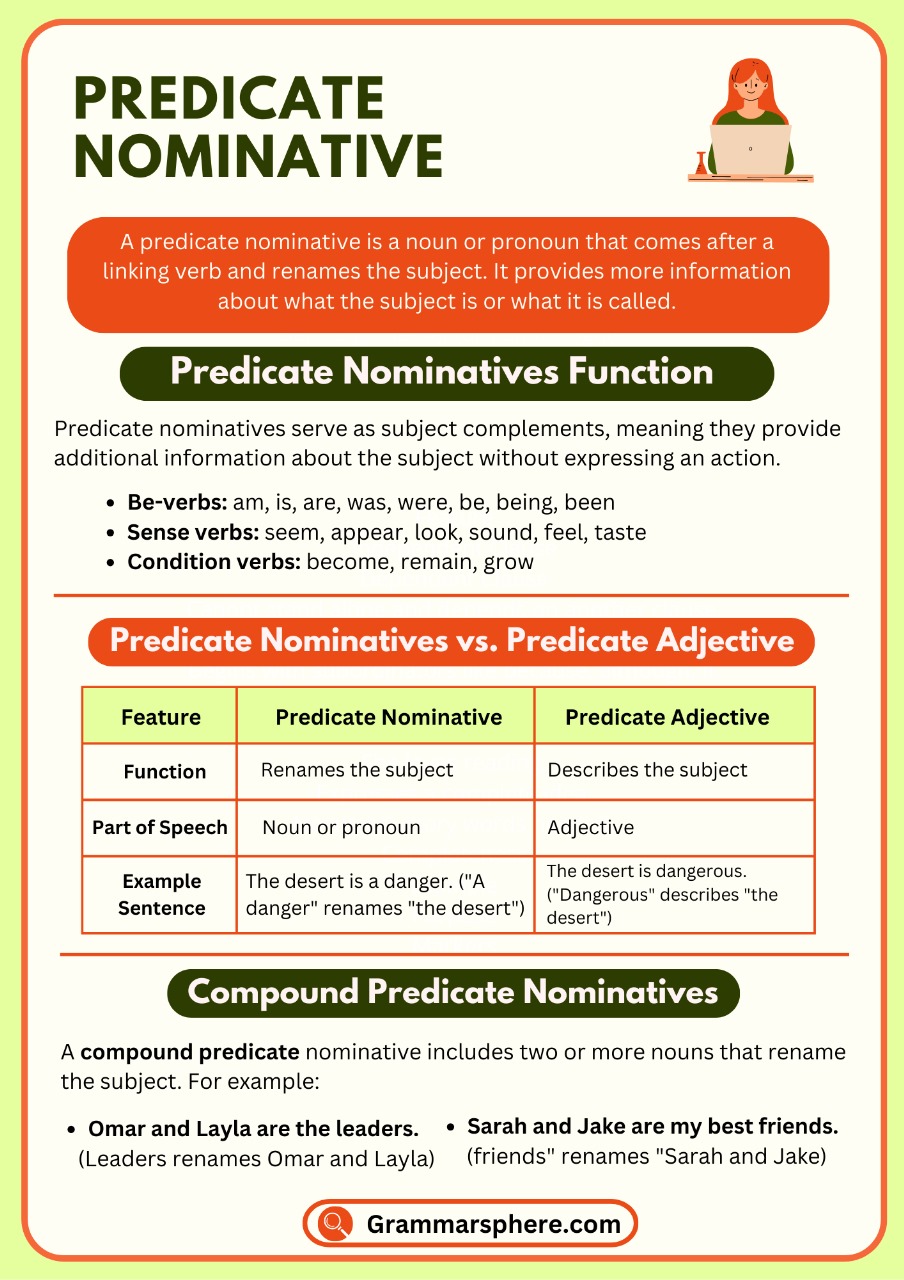
A predicate nominative is a noun or pronoun that follows a linking verb and renames or identifies the subject of a sentence. It provides more information about the subject without performing an action.
Understanding predicate nominatives helps improve sentence clarity and structure, making communication more effective.
What is a Predicate Nominative?
For Example:
Ayesha is a doctor.
In this sentence: Ayesha is the subject. Is is the linking verb.
Doctor is the predicate nominative because it renames Ayesha.
How to Use a Predicate Nominative
A predicate nominative is a noun or pronoun that follows a linking verb and renames the subject, providing more information about it.
1. Use a Linking Verb
A predicate nominative always comes after a linking verb, such as is, was, were, become, seem.
2. It Renames the Subject
It identifies the subject rather than describing it.
✅ The winner was Ali.
(Ali renames winner after the linking verb was.)
❌ The winner was happy.
(Happy is a predicate adjective, not a predicate nominative.)
3. Keep Subject and Predicate Nominative in the Same Case
Use a subject pronoun after a linking verb.
✅ The person responsible is he.
❌ The person responsible is him.
4. Predicate Nominatives in Questions
They can also appear in questions.
✅ Who is the leader? (Leader renames who.)
✅ What was the reason? (Reason renames what.)
Rules for Using Predicate Nominatives
To use a predicate nominative correctly, follow these rules:
1. It follows a linking verb
A predicate nominative always comes after a linking verb.
Example:
Bilal is a teacher.
(Here, teacher renames Bilal after the linking verb is.)
2. It renames or identifies the subject
A predicate nominative must rename or identify the subject, not describe it.
Example:
My father became a businessman.
(Here, businessman renames father after the linking verb became.)
3. It must be a noun or pronoun
A predicate nominative should always be a noun or pronoun.
Example:
The winner was he.
(Here, he is the subject pronoun, correctly used after the linking verb was.)
4. It never follows an action verb
A predicate nominative must follow a linking verb, not an action verb.
Incorrect:
Ahmed plays a musician.
(This is incorrect because plays is an action verb, not a linking verb.)
Correct:
Ahmed is a musician.
(Here, musician is the predicate nominative, following the linking verb is.)
Common Linking Verbs That Introduce Predicate Nominatives
| Linking Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Is | Hina is a nurse. |
| Are | They are my friends. |
| Was | Salman was a student. |
| Were | The twins were actors. |
| Become | He became a leader. |
| Seem | This plan seems a failure. |
Predicate Nominative vs. Predicate Adjective
A predicate nominative is a noun or pronoun, while a predicate adjective is an adjective that describes the subject.
| Type | Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Predicate Nominative | Sarah is a singer. | Singer = noun, renaming Sarah |
| Predicate Adjective | Sarah is talented. | Talented = adjective, describing Sarah |
| Predicate Nominative | John is a teacher. | teacher= noun renaming John |
| Predicate Adjective | John is tired. | Tired= Adjective, describing John |
Predicate Nominative in Questions
Predicate nominatives also appear in questions, often by reordering the sentence.
| Question | Predicate Nominative |
| Who is the captain? | Captain = Predicate Nominative |
| What was the reason? | Reason = Predicate Nominative |
What is a Compound Predicate Nominative?
A compound predicate nominative is a grammatical structure where two or more nouns or noun phrases, connected by a conjunction, rename or identify the subject of the sentence. These nouns follow a linking verb (e.g., is, are, was, were) and provide additional information about the subject, clarifying or describing it.
- Sentence: My mother and father are doctors.
- Subject: My mother and father
- Linking Verb: are
- Compound Predicate Nominative: doctors
Here, the compound predicate nominative doctors renames the subject my mother and father through the linking verb are.
Linking Verbs vs Actions Verbs
| Feature | Linking Verb | Action Verb |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects the subject to more information (e.g., predicate nominative or adjective) | Shows what the subject does (physical or mental action) |
| Predicate | Followed by a predicate nominative or predicate adjective | Followed by a direct object or indirect object |
| Examples | She is a teacher. / The sky appears blue. | She writes a letter. / Tom runs every morning. |
| Function | Does not show action; links the subject to a description or identification | Shows an action performed by the subject |
| Common Verbs | is, am, are, was, were, seem, appear, become | run, jump, eat, think, write, sing |
Common Mistakes with Predicate Nominatives
1. Using an Object Pronoun Instead of a Subject Pronoun
A predicate nominative must be in the subject form, not the object form.
- The winner was him. ❌
- The winner was he. ✅
2. Confusing Predicate Nominative with a Direct Object
A direct object follows an action verb, while a predicate nominative follows a linking verb.
- She named her daughter a doctor. (Direct object) ❌
- She is a doctor. (Predicate nominative) ✅
3. Using Adjectives Instead of a Noun or Pronoun
A predicate nominative must be a noun or pronoun, not an adjective.
- The captain of the team is strong. (Predicate adjective) ❌
- The captain of the team is a leader. (Predicate nominative) ✅
4. Mismatching Singular and Plural Forms
The subject and predicate nominative should agree in number.
- My favorite food is pizzas. ❌
- My favorite food is pizza. ✅
5. Forgetting That Predicate Nominatives Rename the Subject
A predicate nominative must rename or define the subject, not describe it.
- The book is interesting. (Predicate adjective) ❌
- The book is a mystery novel. (Predicate nominative) ✅
FAQs
1. Can a sentence have more than one predicate nominative?
Example: My brothers are doctors and engineers.
2. Can a proper noun be a predicate nominative?
Example: That man is Ali.
3. What is the difference between a predicate nominative and a direct object?
Predicate Nominative: Mary is a lawyer. (Renames Mary)
Direct Object: Mary called a lawyer. (Lawyer is the object of called)
4. Does every sentence have a predicate nominative?
5. Can a sentence be complete without a predicate nominative?
Conclusion
Understanding predicate nominatives improves grammar skills and sentence clarity. They follow linking verbs and rename the subject. By identifying and using them correctly, learners can create stronger and clearer sentences in English. Keep practicing with different examples to master this concept!
You May Also Like





Leave a Comment