Table of Contents
In this blog post, you will learn about prepositions in English, which are words that show the relationship between nouns, pronouns, and other words in a sentence. Prepositions help indicate direction, place, time, and more, making your sentences clear and meaningful.
There are different types of prepositions, such as those of time, place, direction, and manner. We will cover their definitions, types, uses, and provide simple examples for better understanding.
What are Prepositions?
Prepositions are words that link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other parts of a sentence. Their primary function is to show the relationship between these elements, helping clarify things like time, place, direction, or cause.
For example:
The keys are on the table.
The painting is above the sofa.
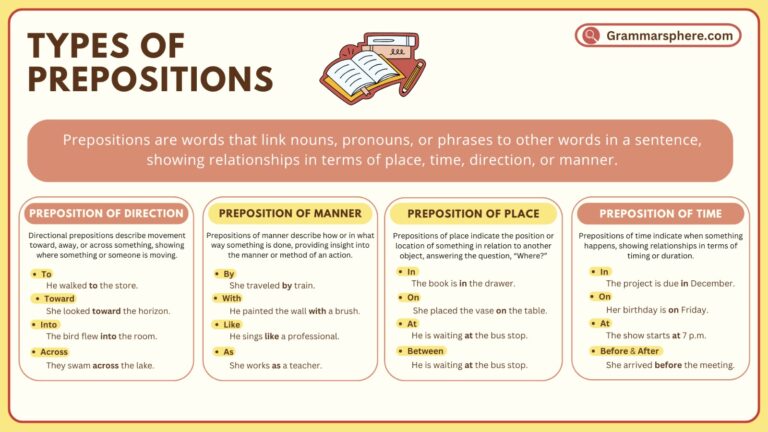
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized based on the kind of relationship they express. Here are the most common types:
1. Prepositions of Place and Position
These prepositions indicate the position or location of something with something else.
- The phone is on the table.
- She stood between the two chairs.
- They hid under the bed.
These words help answer the question: Where?
2. Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time explain when something happens. They are essential for providing temporal context.
- The meeting starts at 3 p.m.
- She was born on Monday.
- We’ll visit in December.
As a general rule, use at for specific times, on for specific days or dates, and in for longer periods like months or years.
3. Prepositions of Direction or Movement
These prepositions indicate movement or direction from one place to another.
- He walked into the room.
- She moved to another city.
- They ran out of the building.
Prepositions of movement help answer the question: Where to? They often follow action verbs to indicate a change in position.
if you want to Learn more about prepositions, click here.

Rules for Using Prepositions
1. A Preposition Must Have an Object
A preposition should always be followed by a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to complete its meaning.
✔ I am going to the market.
✔ She is sitting beside him.
2. Avoid Ending Sentences with a Preposition
In formal English, avoid ending sentences with a preposition. Restructure instead.
✔ This is the place where I grew up.
✘ This is the place I grew up at.
3. Don’t Use Unnecessary Prepositions
Extra prepositions make sentences awkward.
✔ She discussed the project with me.
✘ She discussed about the project with me.
4. Use Specific Prepositions with Certain Verbs
Some verbs require specific prepositions. Learn common verb-preposition pairs.
✔ He apologized for his mistake.
✔ We are waiting for the bus.
5. Prepositions in Questions
In informal English, prepositions often come at the end. In formal English, keep them before the object.
✔ Informal: Who are you going with?
✔ Formal: With whom are you going?
6. Prepositions and Gerunds
A preposition is usually followed by a gerund (-ing verb), not an infinitive (to + verb).
✔ She is interested in swimming.
✘ She is interested in swim.
Common Mistakes with Prepositions
Prepositions can be tricky, and even advanced learners sometimes make mistakes. Let’s look at some common errors and how to avoid them.
1. Using the Wrong Preposition
Some types of verbs require specific prepositions, and using the wrong one can change the meaning.
- Incorrect: She depends in her brother.
- Correct: She depends on her brother.
2. Omitting Necessary Prepositions
Leaving out a preposition can make sentences unclear or grammatically incorrect.
- Incorrect: We are going school.
- Correct: We are going to school.
3. Adding Unnecessary Prepositions
Sometimes, extra prepositions are added out of habit, even though they are not needed.
- Incorrect: Where are you at?
- Correct: Where are you?
FAQS
What is a preposition and examples
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. It often indicates direction, place, time, or manner.
Examples:
Time: She arrived after lunch.
Place: The book is on the table.
Direction: He walked toward the park.
Manner: She spoke with confidence.
What is the 10 example of preposition?
The keys are in the drawer. She placed the book on the table. We will meet at 5 PM. He stood by the window. She wrote with a pen. This gift is for you. She walked to the store. He traveled from New York. The cat is under the chair. The park is between the school and the mall.
What are the 24 prepositions?
in, on, at, by, with, for, to, from, under, between, over, above, below, near, beside, behind, before, after, during, inside, outside, along, against, through.
What are Preposition Rules?
Always followed by a noun/pronoun – She sat on the chair.
Shows relationships (place, time, direction) – Book is on the table.
Cannot stand alone – He is looking for his keys.
Avoid at sentence end (formal writing) – “Where are you?” (Not “Where are you at?”)
Some words need specific prepositions – “Interested in,” “Good at.”
Time prepositions: at 5 PM, on Monday, in June.
Place prepositions: at the door, on the table, in the room.
You May Also Like





Leave a Comment