Table of Contents
Many English learners find the present perfect tense confusing. When do you use “have” or “has”? How is it different from the past tense? This blog post helps learn present perfect tense with clear rules, structure, and common mistakes to avoid. By mastering this tense, you’ll improve your ability to talk about past actions with present relevance.
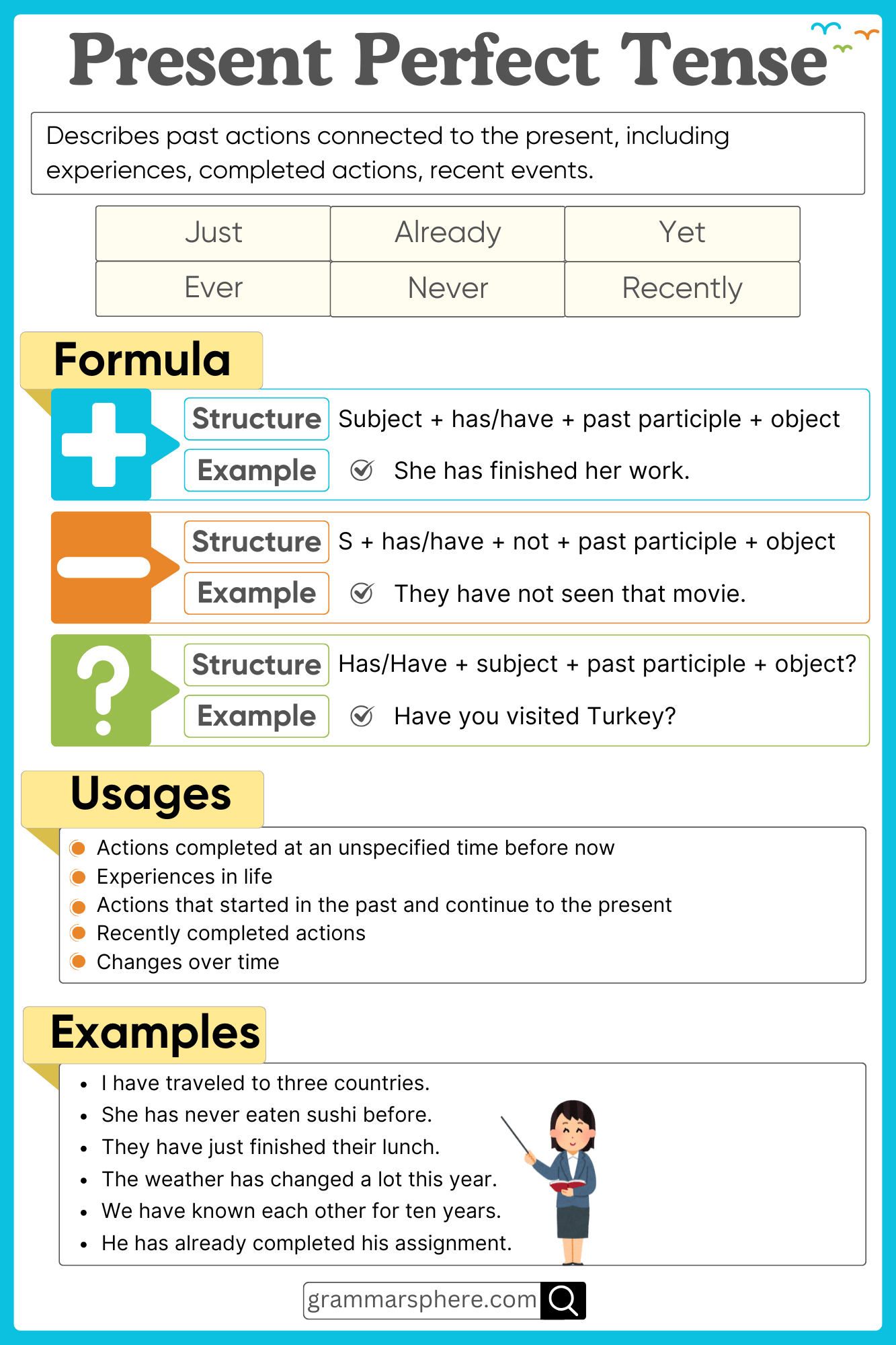
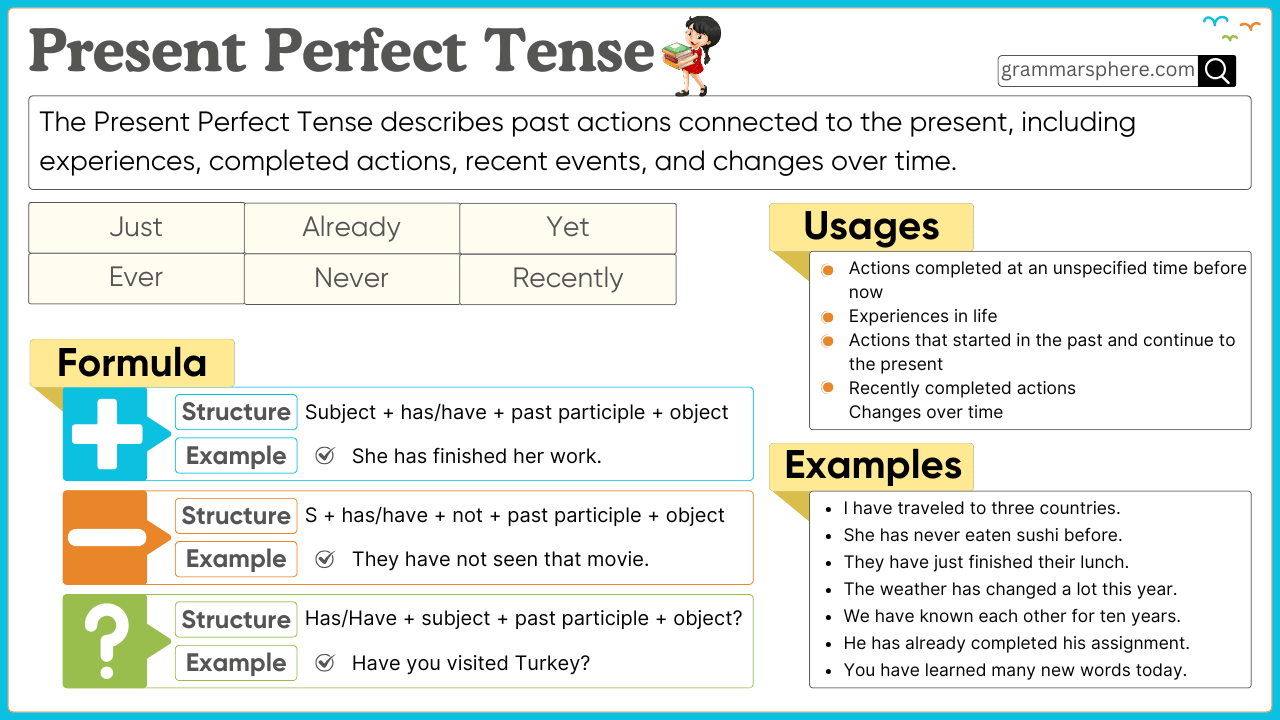
What is Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past or started in the past and continue into the present. This tense helps us express experiences, changes, and unfinished actions.
Structure of the Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using:
Subject + has/have + past participle (V3)
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have + past participle + object
- Aisha has visited Turkey.
- They have completed their homework.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have + not + past participle + object
- Aisha has not visited Turkey.
- They have not completed their homework.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Has/Have + subject + past participle + object?
- Has Aisha visited Turkey?
- Have they completed their homework?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + has/have + subject + past participle + object?
- Where has Aisha visited?
- Why have they completed their homework early?
Subject-Verb Agreement
The helping verb changes depending on the subject:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| I/We/You/They | have |
| He/She/It | has |
Time Expressions in Present Perfect Tense
These words indicate when the action happened:
- Ever/Never: Have you ever traveled abroad?
- Just: I have just finished my work.
- Already: She has already left.
- Yet: They haven’t arrived yet.
- Since/For: He has lived here since 2010.
Adverb Placement in Present Perfect
1. Before the Past Participle
Adverbs like already, just, ever go before the past participle to show time or emphasis.
- She has already finished her meal. (The action is completed earlier than expected.)
2. After the Object
Adverbs like carefully, well, thoroughly come after the object to describe how the action was done.
- They have studied the lesson carefully. (Explains the manner of studying.)
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
1. Actions that happened at an unspecified time
Used for past actions without mentioning an exact time.
- Bilal has visited Makkah. (The exact time is unknown or not important.)
2. Actions that started in the past and continue
Describes actions that began earlier and are still ongoing.
- Ahmed has lived in Karachi for ten years. (He still lives there.)
3. Life experiences
Used to talk about experiences someone has had or not had.
- I have never eaten sushi. (At no point in my life have I tried it.)
4. Recent past actions
Shows actions that happened very recently, often with just.
- They have just arrived. (They arrived a short time ago.)
5. Repeated actions
Indicates actions that have happened multiple times.
- She has watched that movie three times. (She has done it more than once.)
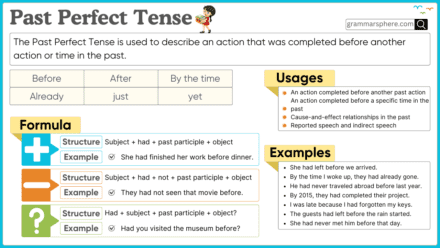
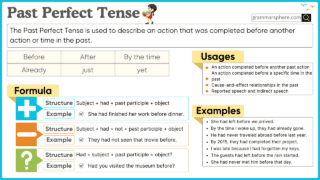
Present Perfect vs Past Perfect Tense
| Feature | Present Perfect | Past Perfect |
| Auxiliary Verb | has/have | had |
| Action Timing | Past to Present | Before another past event |
| Example | She has eaten lunch. | She had eaten lunch before I arrived. |
Examples of the Present Perfect Tense in Use
Affirmative Sentences
- Aisha has completed her homework.
- We have watched that movie twice.
- Omar has visited his grandparents this month.
- They have bought a new house.
- He has learned Arabic.
Negative Sentences
- Sarah has not cooked dinner yet.
- We have not seen that new restaurant.
- Ahmad has not called me today.
- The children have not finished their assignments.
- You have not traveled to Turkey.
Interrogative Sentences
- Has your sister found her lost book?
- Have they arrived at the airport?
- Has Hamza completed his report?
- Have we met before?
- Has she decided on a university?
Common Mistakes with the Present Perfect Tense
❌ He has go to school.
✅ He has gone to school.
❌ We have finish our work.
✅ We have finished our work.
❌ She has lived here since five years.
✅ She has lived here for five years.
FAQs
When do we use the Present Perfect Tense?
We use it for unspecified past actions, experiences, and actions continuing into the present.
What is the difference between Present Perfect and Past Simple?
Present Perfect is used when the time is not mentioned, while Past Simple is used when the time is specified.
Can we use Present Perfect with specific time expressions?
No, we do not use it with yesterday, last year, in 2010, etc.
Read More





Leave a Comment