Table of Contents
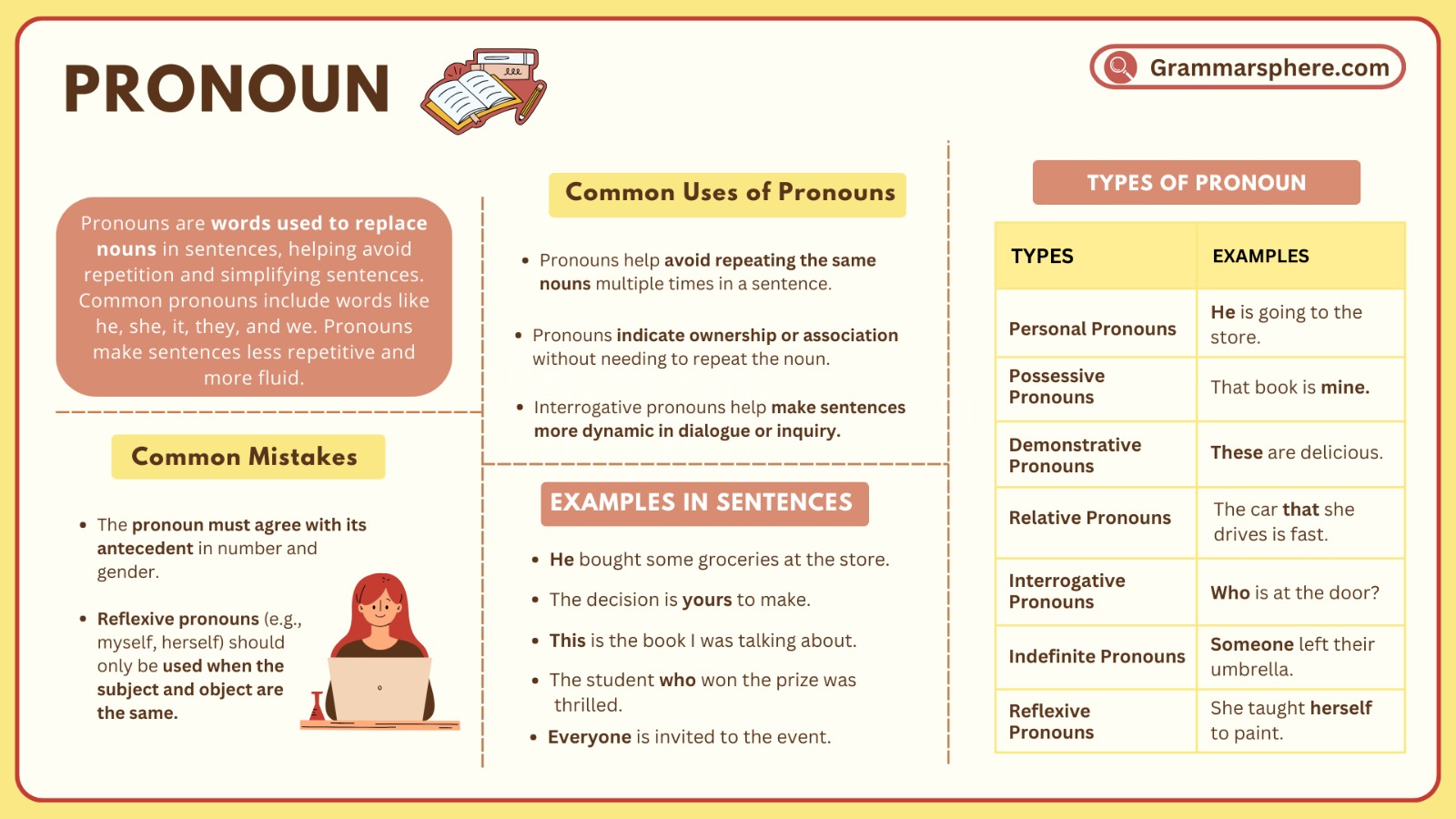
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother. Examples include he, she, it, they, and we. Pronouns help in referring to people, places, or things without repeating names. They make speech and writing clearer and more natural.
What is A Pronoun?

A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun in a sentence. It helps avoid repetition and makes sentences clearer..
Example Sentences:
They went to the park because they wanted to play.
She loves to read books, especially when she is alone.
We have finished our work, so we can go home now.
It was raining heavily, but it stopped in the evening
Pronouns List
- I
- You
- He
- She
- It
- We
- They
- Me
- Him
- Her
- Us
- Them
- My
- Your
- His
- Her
- Its
- Our
- Their
Types of Pronoun
- Personal Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Reciprocal Pronouns
- Intensive Pronouns
1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are referred to specific people or things and can act as the subject or object in a sentence.
- He is studying hard for his exams.
- They went to the store to buy groceries.
- She loves spending time at the library.
- We are planning a surprise party for our friend.
- I will call you later tonight.
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to show ownership or possession of something.
- The book is mine, not yours.
- His idea was the best in the meeting.
- The decision is ours to make.
- Their car broke down on the way to work.
- That house is hers.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of the sentence are the same person or thing, reflecting back on the subject.
- She prepared the meal by herself.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party.
- He looked at himself in the mirror.
- We will handle it ourselves.
- I taught myself to play the guitar.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to specific items or people and can be used to indicate proximity or distance.
- This is my favorite book.
- That looks interesting.
- These are my friends from college.
- Those were the days we enjoyed the most.
- This is the house I grew up in.
5. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions, helping us gather more information.
- Who is coming to the event?
- What do you want to eat?
- Which one would you prefer?
- Whom did you talk to yesterday?
- Whose is this bag?
6. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are used to introduce clauses that provide more information about a noun mentioned earlier. They help connect ideas within a sentence.
- The book that you gave me was fascinating.
- She’s the person who helped me find my way.
- This is the house where I grew up.
- I have a friend whose brother is a famous musician.
- The cake, which he baked, was delicious.
7. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people, places, or things. They are often used to generalize rather than specify.
- Everyone enjoyed the concert.
- Something is missing from the shelf.
- Nobody knew the answer to the question.
- Each of the students received a certificate.
- Anything can happen if we believe.
8. Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are used when two or more people or things are acting in the same way towards each other.
- The two friends respect each other.
- They gave gifts to one another.
- The players congratulated each other after the game.
- We should always support one another.
- The team members trust each other completely.
9. Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns are used to emphasize the subject of the sentence, often adding a stronger focus on who is performing the action.
- The CEO himself presented the award.
- She herself completed the entire project.
- I myself will handle the arrangements.
- They themselves organized the event.
- You yourself made this possible.

Pronouns vs. Nouns
Understanding the difference between pronouns and nouns is essential for clear communication in English. Both play a vital role in sentence structure but serve different purposes.
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It provides specific information about who or what is involved in a sentence.
Examples of nouns:
- Sarah loves to read.
- The city was crowded.
- I bought a new laptop.
- Happiness is important for health.
In these sentences, Sarah, city, laptop, and happiness are nouns because they directly name people, places, things, or ideas.
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother. Instead of repeating a noun, we use a pronoun to refer back to it.
Examples of pronouns:
- She loves to read.
- It was crowded.
- I bought a new one; it works great.
- This is important for health.
Here, she, it, and this are pronouns that take the place of specific nouns mentioned earlier or implied.
Pronoun vs Determiners
Pronouns and determiners may seem similar because they both refer to people, places, or things, but they play different roles in sentences.
What are Pronouns?
Pronouns replace nouns in sentences to avoid repetition and keep sentences clear. They stand alone, taking the place of a specific noun or group of nouns.
Examples of pronouns: he, she, it, they, ours, theirs, someone
Example sentences:
- She is coming to the meeting.
- They went to the park yesterday.
In these examples, the pronouns she and they stand alone and replace specific nouns.
What are Determiners?
Determiners, on the other hand, are words placed before nouns to give more information about them. They do not stand alone but must always accompany a noun. Determiners indicate specifics, quantities, or ownership related to the noun.
Examples of determiners: this, my, some, each, several
Example sentences:
- My book is on the table.
- Each student received a certificate.
- Some people enjoy hiking.
Here, my, each, and some are determiners giving more information about the nouns they accompany (book, student, and people).
Example Sentences with Pronouns
- She is preparing for her final exams this week.
- They are planning a road trip across the country.
- He enjoys reading novels in his free time.
- I have already finished my homework for today.
- We decided to volunteer at the community center.
- It was raining heavily last night.
- You need to submit the report by tomorrow.
- She brought her own lunch to the office.
- They celebrated their anniversary in a cozy restaurant.
- He forgot his umbrella at home.
FAQs About Pronouns
1. What is a pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun, like he, she, or they.
2. What are the types of pronouns?
Common types include personal, possessive, demonstrative, reflexive, and relative pronouns.
3. Why are pronouns important?
Pronouns make sentences less repetitive and improve clarity in speech and writing.
4. What is an example of a pronoun in a sentence?
Instead of saying John is tired, you can say, He is tired.
5. What is the difference between who and whom?
Who is used as a subject (e.g., Who is calling?), while whom is used as an object (e.g., To whom should I speak?).
You May Also Like



Leave a Comment