Table of Contents
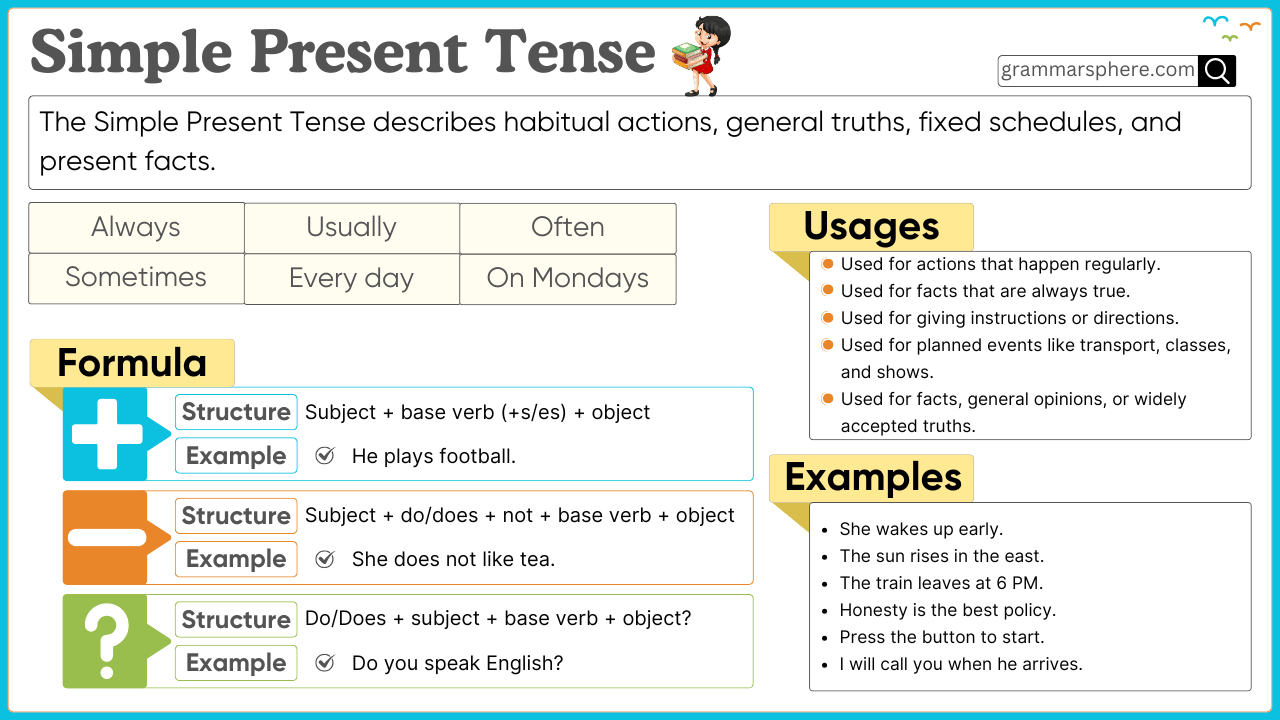
The simple present tense is one of the most commonly used tenses in English. It describes habitual actions, general truths, scheduled events, and instructions. Understanding this tense is essential for forming correct and meaningful sentences. This blog post helps learn the simple present tense with structures, subject-verb agreement, common mistakes, and usage rules.
Structures of the Simple Present Tense
The sentence structure of the simple present tense varies depending on whether the sentence is affirmative, negative, or interrogative.
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + base verb (+s/es for third-person singular) + object
- Aisha reads the Quran daily.
- Ahmed and Yusuf play football every weekend.
In the second sentence, since the subject is plural, the base verb play does not change.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + do/does not + base verb + object
- Fatima does not like spicy food.
- They do not study at night.
For third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), we use does not, while for all other subjects, we use do not.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Do/Does + subject + base verb + object?
- Does Hamza speak Arabic?
- Do the students understand the lesson?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question word + do/does + subject + base verb + object?
- What time does the class start?
- Where do you live?

Subject-Verb Agreement
Correct subject-verb agreement is crucial in the simple present tense. The verb changes based on the subject.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Example Verb (to work) |
|---|---|---|
| I | do | work |
| You | do | work |
| He/She/It | does | works |
| We | do | work |
| They | do | work |
Example:
- Hamza works at a hospital.
- The children play in the park.
Time Expressions in Simple Present Tense
Time expressions help indicate the frequency of an action. Below are common time expressions used with this tense:
- Always: Aisha always wakes up early.
- Usually: Ahmed usually walks to school.
- Often: We often visit our grandparents.
- Sometimes: They sometimes eat out.
- Never: Fatima never skips her prayers.
Adverb Placement
Adverbs of frequency (always, usually, sometimes, never) are placed before the main verb but after the verb “to be”.
- Amina always studies before exams.
- Yusuf is never late.
Uses of the Simple Present Tense
1. Habitual Actions (Repeated Routines)
- Adam prays five times a day.
- We go to the mosque on Fridays.
2. General Truths (Universal Facts)
- The sun rises in the east.
- Water boils at 100°C.
3. Scheduled Events (Fixed Timetables)
- The bus arrives at 7 AM.
- The meeting starts at noon.
4. Instructions or Directions (Step-by-Step Actions)
- First, add sugar to the tea.
- Turn right at the next signal.
Examples of the Simple Present Tense in Use
Affirmative Sentences
- Hamza teaches English.
- The birds sing every morning.
- She writes a letter every Sunday.
- They play football in the evening.
- The train arrives at 8 AM.
Negative Sentences
- She does not watch TV.
- We do not eat junk food.
- He does not like spicy food.
- The baby does not cry at night.
- I do not drink coffee.
Interrogative Sentences
- Does Ahmed like ice cream?
- Do they visit their relatives often?
- Does she wake up early in the morning?
- Do you go to school by bus?
- Does it rain in winter?
Common Mistakes with the Simple Present Tense
| Mistake | Correction |
| He go to school daily. ❌ | He goes to school daily. ✅ |
| They does not like fish. ❌ | They do not like fish. ✅ |
| Does she likes coffee? ❌ | Does she like coffee? ✅ |
FAQs
When do we use the simple present tense?
How do we form negative sentences in the simple present tense?
What is the difference between “do” and “does”?
Can we use adverbs of frequency with the simple present tense?
How do we make questions in the simple present tense?
Read more





Leave a Comment