Table of Contents
The past perfect continuous tense confuses many learners because it describes longer actions that were ongoing before another past event. When should you use “had been” + verb-ing? How does it differ from the past perfect tense? This blog post helps learn past perfect continuous tense with clear rules, structure, and examples. Mastering this tense will improve your ability to talk about past actions with duration.
What is Past Perfect Continuous Tense
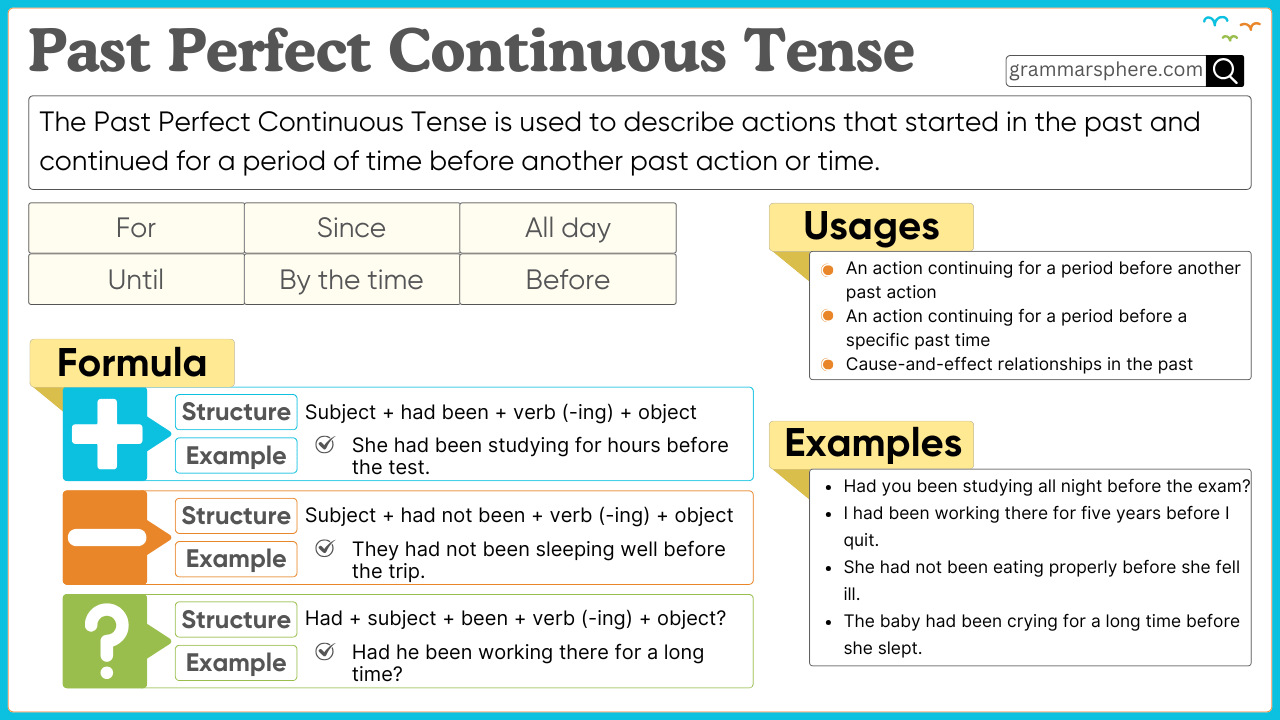
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense describes an action that started in the past, continued for a period, and ended before another past action or time. It emphasizes the duration of the action before another event.
Structure of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is formed using:
Subject + had + been + verb(-ing)
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had been + verb(-ing) + object + time reference
- Aisha had been reading a book for two hours before she fell asleep.
- They had been playing football since morning before the rain started.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had not been + verb(-ing) + object + time reference
- Aisha had not been reading a book for two hours before she fell asleep.
- They had not been playing football since morning before the rain started.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Had + subject + been + verb(-ing) + object + time reference?
- Had Aisha been reading a book for two hours before she fell asleep?
- Had they been playing football since morning before the rain started?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + had + subject + been + verb(-ing) + object + time reference?
- How long had Aisha been reading before she fell asleep?
- Why had they been playing football before the rain started?

Subject-Verb Agreement
The helping verb remains the same for all subjects:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| All Subjects | had been |
Time Expressions in Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Time expressions help indicate how long the action took place before another event:
- For: I had been studying for three hours before the power went out.
- Since: She had been working here since 2015 before she resigned.
- Before: They had been playing football before the match was canceled.
- Until: We had been waiting until the shop opened.
Adverb Placement
- Before the main verb: She had always been studying hard before exams.
- After the object: They had been practicing football seriously before the tournament.
Uses of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
1. To Show the Duration of an Action Before Another Past Event
This tense emphasizes how long an action had been happening before another event in the past.
- Ahmed had been studying for three hours before he took a break.
- They had been waiting for the bus for 30 minutes when it finally arrived.
2. To Explain the Cause of a Past Situation
It is used to show that a past situation was the result of a long action.
- She was exhausted because she had been working all day.
- His clothes were dirty because he had been playing football.
3. To Describe Parallel Continuous Actions in the Past
This tense can describe two actions that were happening simultaneously for a period before another event.
- While Zainab had been cooking, Ahmed had been setting the table.
- They had been discussing the project while the manager had been reviewing the reports.
4. To Emphasize Repeated Actions in the Past
It is used to highlight repeated or habitual actions that happened over a period before another event.
- He had been calling her every day before she finally answered.
- They had been practicing for months before the final performance.
Past Perfect Continuous vs Past Perfect Tense
| Feature | Past Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect |
| Auxiliary Verb | had been | had |
| Emphasis | Duration of action | Completed action |
| Example | She had been reading a book for two hours before she fell asleep. | She had read a book before she fell asleep. |
Examples of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Fatima had been cooking dinner for an hour before the guests arrived.
- We had been working on this project since morning before the meeting.
- The baby had been crying before his mother picked him up.
- The teacher had been explaining the topic before the bell rang.
- The students had been waiting for the exam results before they were announced.
Negative:
- Bilal had not been sleeping well before his exams.
- They had not been attending classes regularly before the final test.
- She had not been working on the assignment before the deadline.
- We had not been practicing enough before the tournament.
- I had not been studying properly before the mock test.
Interrogative:
- Had your brother been studying before the test?
- Had they been exercising daily before the event?
- Had she been working on the project before the submission date?
- Had he been learning Arabic before traveling?
- Had we been waiting for long before the gates opened?
Common Mistakes with the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
1. Using “Play” Instead of “Playing”
❌ He had been play football before it rained.
✅ He had been playing football before it rained.
2. Incorrect Verb Form After “Had Been”
❌ We had been finish our work before the deadline.
✅ We had been finishing our work before the deadline.
3. Wrong Use of “Lived” Instead of “Living”
❌ She had been lived here before moving abroad.
✅ She had been living here before moving abroad.
FAQs
When do we use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
We use it for actions that started in the past, continued for a period, and ended before another past action.
What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous?
Past Perfect focuses on completed actions, while Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes the duration of an action before another past event.
Can we use stative verbs in Past Perfect Continuous?
No, verbs like know, believe, love, hate are not used in this tense.
Read More






Leave a Comment