Table of Contents
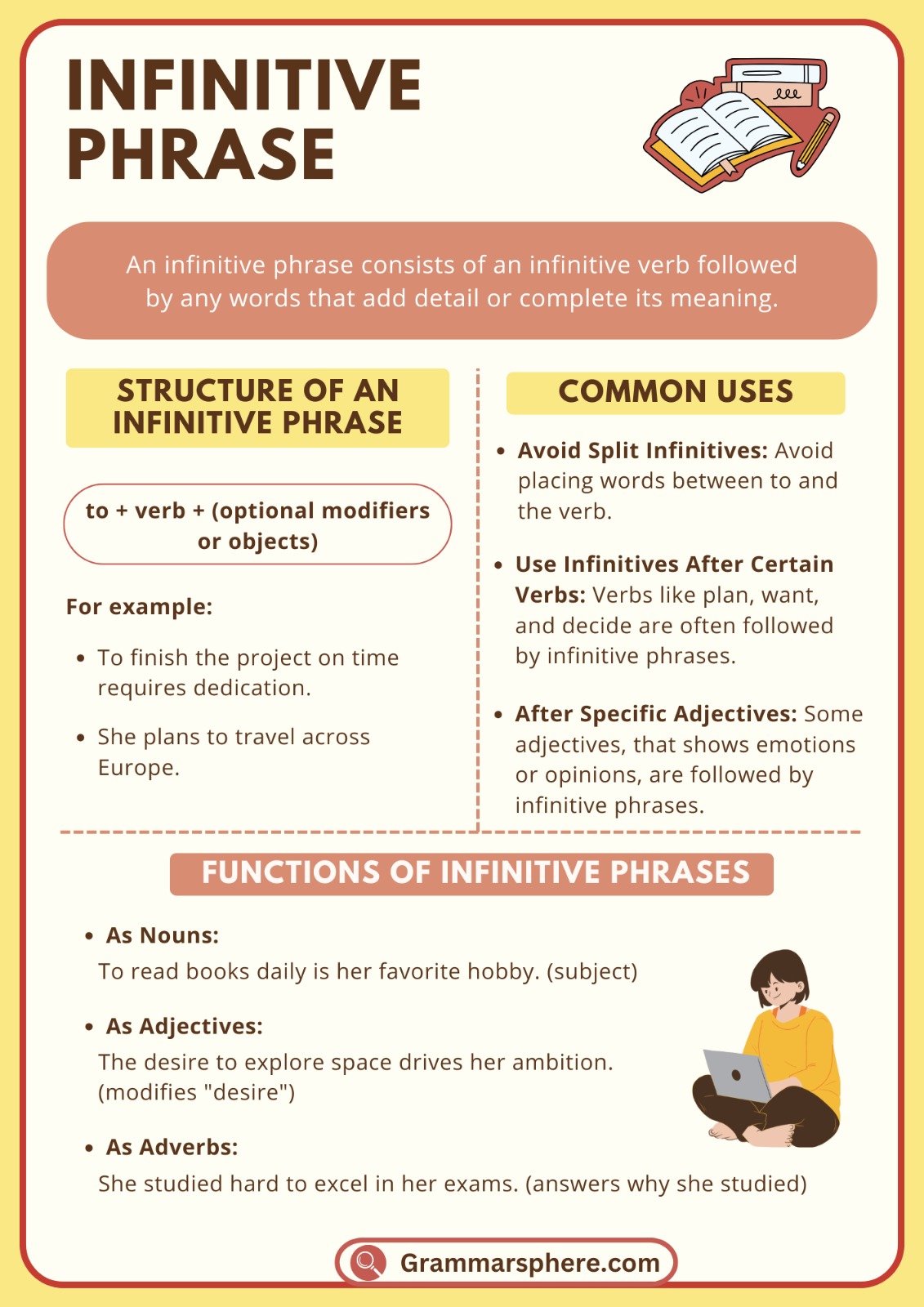
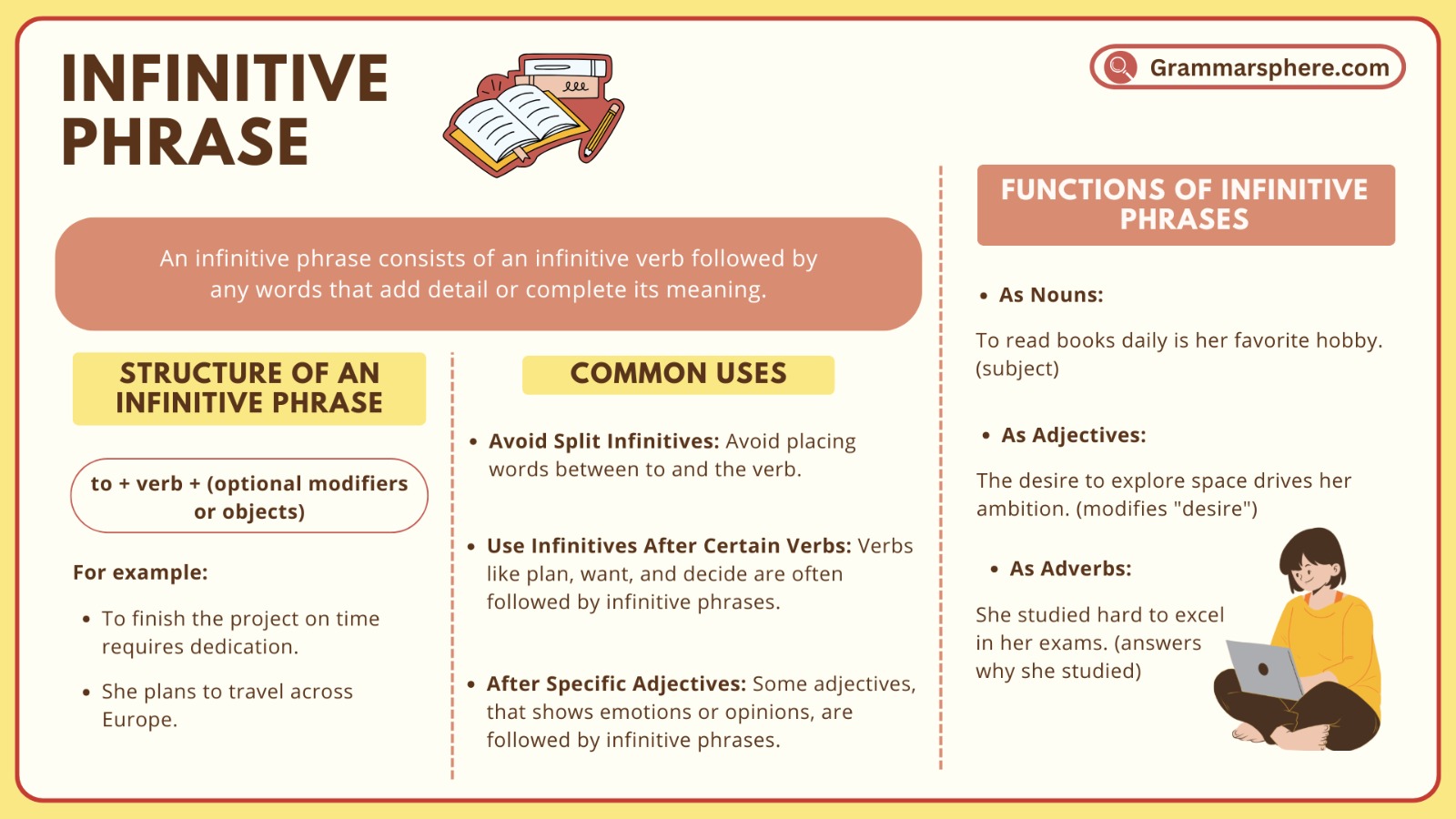
An infinitive phrase consists of the word to followed by the base form of a verb. This phrase can act as a noun, adjective, or adverb in a sentence. Infinitive phrases help express purposes or goals, making sentences more clear and detailed.
They are useful for describing actions or intentions, allowing you to communicate more effectively in both writing and speaking.
What is infinitive Phrase?
An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive verb followed by any words that add detail or complete its meaning.
Examples:
To finish the project on time was our goal.
She wants to travel the world.
They came here to learn English.
Function of infinitive phrase
1. Infinitive Phrase as a Noun
When an infinitive phrase functions as a noun, it acts as the subject or object of a sentence, answering what or who. It can serve as the main focus of the sentence or as a complement to a verb.
- She hopes to win the competition.
- His dream is to travel the world.
2. Infinitive Phrase as an Adjective
As an adjective, an infinitive phrase describes or gives more detail about a noun, helping to clarify or specify something about that noun.
- She has a book to read for class.
- He made a list to organize his tasks.
3. Infinitive Phrase as an Adverb
When used as an adverb, an infinitive phrase explains why or how something is done, often indicating purpose.
- She went to the library to study quietly.
- They practice daily to improve their skills.
Infinitive Phrases vs Prepositional Phrases
| Feature | Infinitive Phrase | Prepositional Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Begins with “to” + base verb | Begins with a preposition + noun/pronoun |
| Function | Acts as a noun, adjective, or adverb | Shows location, time, direction, or relationship |
| Contains a Verb? | ✅ Yes (always includes a verb) | ❌ No (never contains a verb) |
| Example 1 | She wants to learn Spanish. | The book is on the table. |
| Example 2 | He loves to play football. | The keys are under the sofa. |
What are Types of infinitives
Here are three main types of infinitives– simple infinitives, perfect infinitives, and continuous infinitives. Each type helps convey different meanings and time frames.
1. Simple Infinitive:
This is the most common form, using to plus the base verb. It expresses general actions or states.
- She wants to learn Spanish.
2. Perfect Infinitive:
This form uses to have plus the past participle of a verb. It shows an action that happened before another action or is completed.
- He seems to have finished his homework already.
3. Continuous Infinitive:
This uses to be plus the -ing form of a verb, describing an action that is ongoing or happening at the same time as another action.
- They appear to be waiting for the bus.
4. Full Infinitive
A full infinitive (also called a to-infinitive) consists of “to” + base verb (e.g., to eat, to study, to go). It can function as a noun, adjective, or adverb in a sentence.
Usages of Full Infinitives
1. To Express Purpose → She went to the store to buy milk.
2. After Certain Verbs → She wants to learn French.
3. After Adjectives → She is excited to start her new job.
4. After Nouns or Pronouns → I need a book to read.
5. After Question Words → She knows how to cook.
5. Bare Infinitives
A bare infinitive is the base form of a verb without “to” (e.g., go, see, do, run). It is used in specific grammatical structures.
Usages of Bare Infinitives
- After Modal Verbs → She can swim very well.
- After Verbs of Perception → I heard him sing a beautiful song.
- After “Let” and “Make” → The teacher made us write the answer on the board.
- After “Had Better” and “Would Rather” → You had better leave before it gets dark.
- After “Why” in Questions → Why wait when you can start now?
Example Sentences with Infinitive Phrases
- She hopes to travel the world someday.
- He promised to complete his work on time.
- They decided to start a new project together.
- The teacher encouraged us to read more books.
- She went to the library to find more information.
- He tried to solve the problem quickly.
- We were excited to meet our favorite author.
- The team worked hard to achieve their goals.
- She offered to help with the decorations.
- They need to practice regularly for the performance.
infinitives vs Gerund
| Feature | Infinitive | Gerund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | “To” + base verb (e.g., to eat, to run) | -ing form of a verb (e.g., eating, running) |
| Function | Acts as a noun, adjective, or adverb | Acts only as a noun |
| Verb Form | Base form of the verb | Present participle (-ing form) |
| Examples | I want to go to the park. (Noun) | I love swimming in the pool. (Noun) |
| = | He is ready to help us. (Adjective modifier) | She enjoys reading books. (Noun) |
| = | She left early to catch the train. (Adverb modifier) | Swimming is a great exercise. (Noun) |
You May Also Like





Leave a Comment