Table of Contents
Many learners struggle with the present perfect continuous tense because it combines past and present actions. When should you use has been or have been? How does it differ from the present perfect tense? This blog post helps learn present perfect continuous tense with clear rules, structure, and common mistakes to avoid. By mastering this tense, you’ll describe ongoing actions more accurately in English.
What is Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
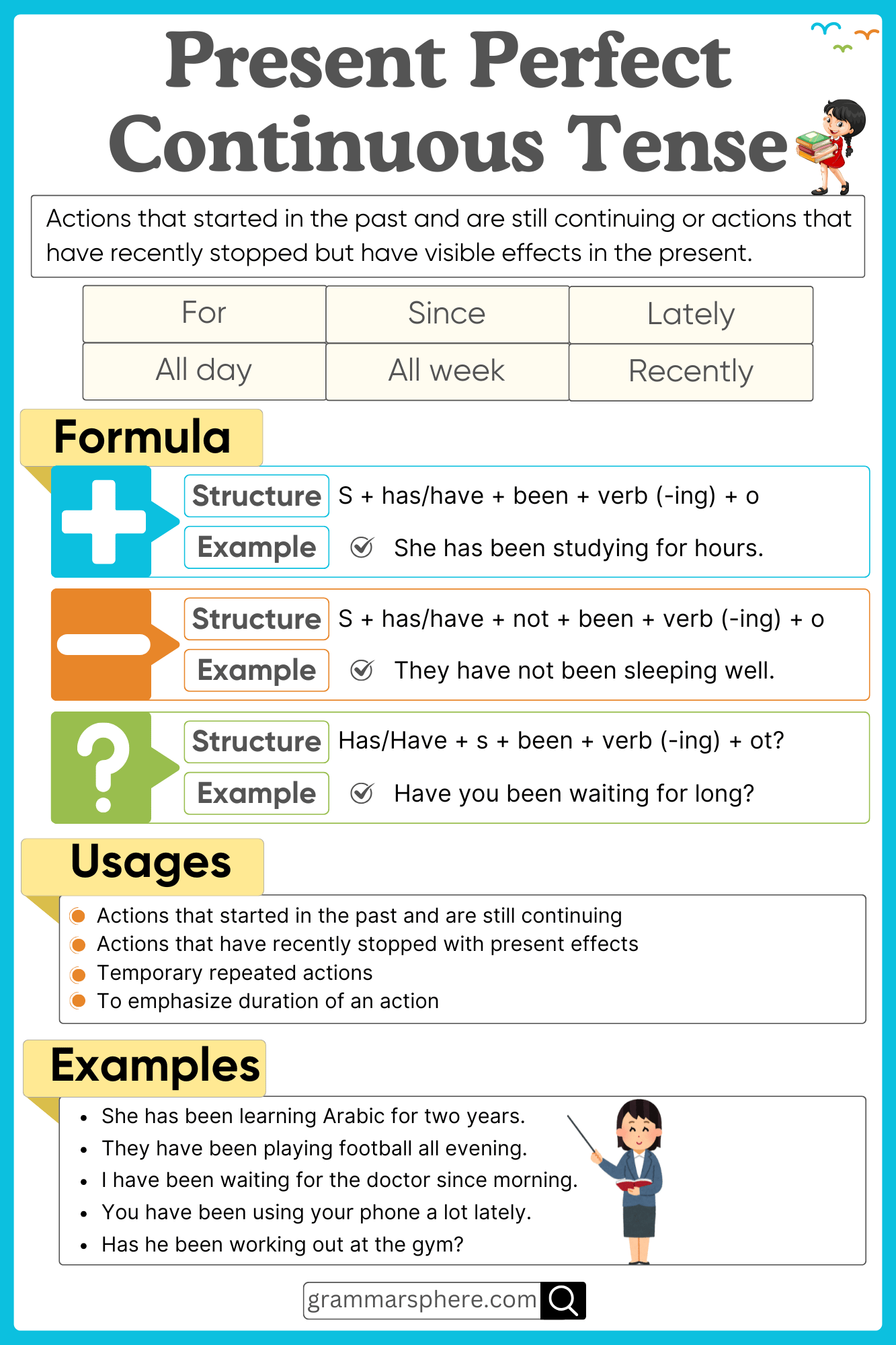
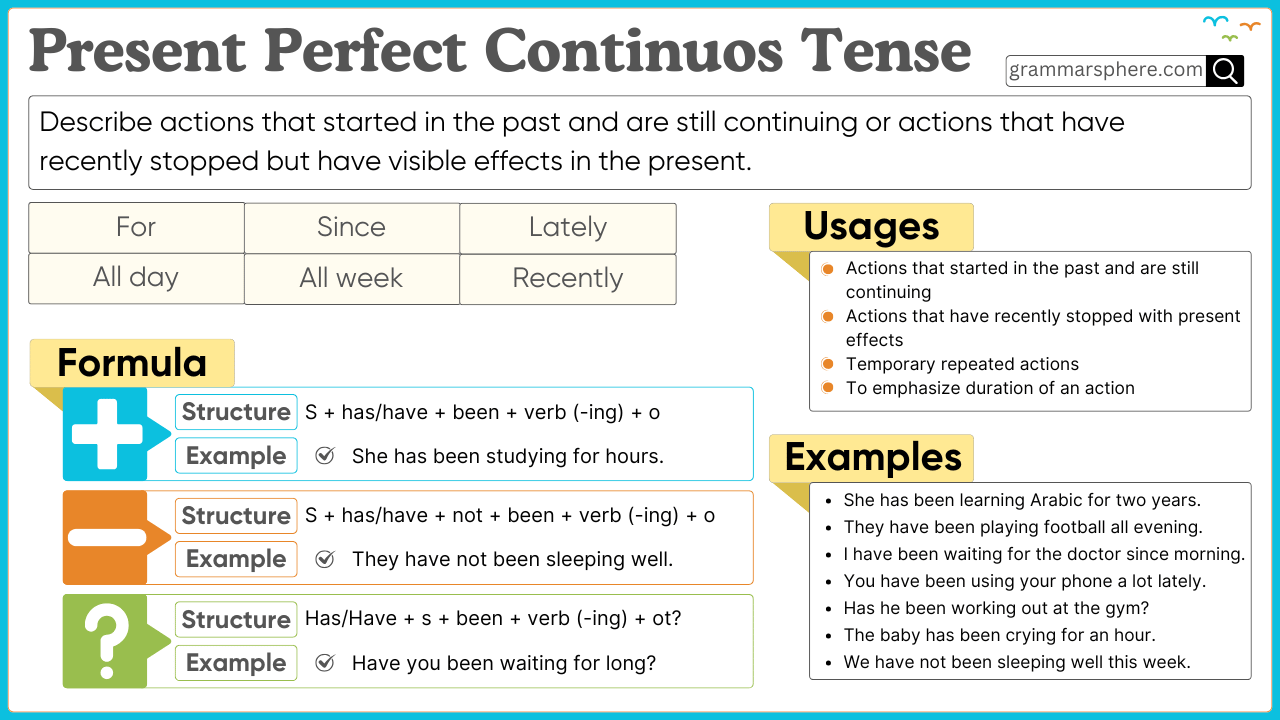
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense describes actions that began in the past and are still continuing or recently stopped but have an effect on the present. It emphasizes the duration of an action.
Structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is formed using:
Subject + has/have + been + verb(-ing)
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have + been + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha has been reading a book for two hours.
- They have been playing football since morning.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have + not + been + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha has not been reading a book for two hours.
- They have not been playing football since morning.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Has/Have + subject + been + verb(-ing) + object?
- Has Aisha been reading a book for two hours?
- Have they been playing football since morning?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + has/have + subject + been + verb(-ing) + object?
- How long has Aisha been reading?
- Why have they been playing football?
Subject-Verb Agreement
The helping verb changes depending on the subject:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| I/We/You/They | have been |
| He/She/It | has been |
Time Expressions in Present Perfect Continuous Tense
These words indicate how long the action has been happening:
- For: I have been studying for three hours.
- Since: She has been working here since 2020.
- Lately/Recently: They have been feeling tired lately.
Adverb Placement
In the Present Continuous Tense, adverbs are usually placed before the main verb (verb+ing) or between the auxiliary verb (am/is/are) and the main verb.
1. Before the main verb
- He is constantly talking.
- They are always arguing.
2. Between the auxiliary verb and the main verb
- She is slowly learning English.
- We are carefully planning our trip.
3. At the beginning or end of the sentence (less common)
- Suddenly, he is running toward us.
- She is looking at me angrily.
Uses of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
1. Actions that started in the past and continue in the present
This tense is used for actions that began in the past and are still happening.
- Ahmed has been living in Dubai for five years.
- They have been working on this project since Monday.
2. Actions that recently stopped but have present effects
It describes actions that have just ended but left visible results.
- She has been crying, so her eyes are red.
- Ali has been running, and now he is out of breath.
3. Emphasizing duration
This tense highlights how long an action has been happening.
- Bilal has been waiting for an hour.
- I have been studying all day.
Present Perfect Continuous vs Present Perfect Tense
| Feature | Present Perfect Continuous | Present Perfect |
| Auxiliary Verb | has/have been | has/have |
| Emphasis | Duration of action | Completed action |
| Example | She has been reading a book for two hours. | She has read a book. |
Examples of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative Sentences:
- Ayesha has been reading a novel for two hours.
- The children have been playing in the park since evening.
- Ahmed has been writing a poem since morning.
- We have been learning English for several months.
- The teacher has been explaining the lesson for an hour.
Negative Sentences:
- Sarah has not been feeling well since yesterday.
- The boys have not been practicing for the match.
- He has not been completing his assignments on time.
- We have not been visiting our grandparents lately.
- The baby has not been sleeping peacefully at night.
Interrogative Sentences:
- Has Fatima been cooking since morning?
- Have they been waiting for the bus for long?
- Has he been listening to music all day?
- Have the students been preparing for the exam?
- Has your mother been talking to the doctor?
Common Mistakes with the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
❌ He has been play football for two hours.
✅ He has been playing football for two hours.
❌ We have been finish our work.
✅ We have been finishing our work.
❌ She has been lived here since 2015.
✅ She has been living here since 2015.
FAQs
When do we use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
We use it for actions that started in the past and continue into the present and recent actions with present effects.
What is the difference between Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous?
Present Perfect focuses on completed actions, while Present Perfect Continuous emphasizes the duration of an ongoing action.
Can we use stative verbs in Present Perfect Continuous?
No, verbs like know, believe, love, hate are not used in this tense.
Read More




Leave a Comment