Table of Contents
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They help indicate direction, place, time, manner, cause, and more. Common types include prepositions of place (in, on, under), time (before, after, during), direction (to, from, into), and manner (by, with, like). Understanding prepositions makes sentences clearer and improves communication in English.
What is A Preposition?
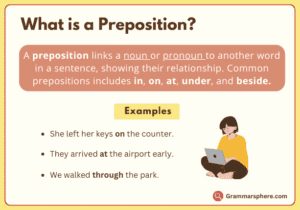
A preposition connects a noun or pronoun to another word in a sentence, showing their relationship and helping to clarify details like time, place, or direction.
Examples:
She left her keys on the counter.
The cat hid under the sofa.
They arrived at the airport early.
We walked through the park.
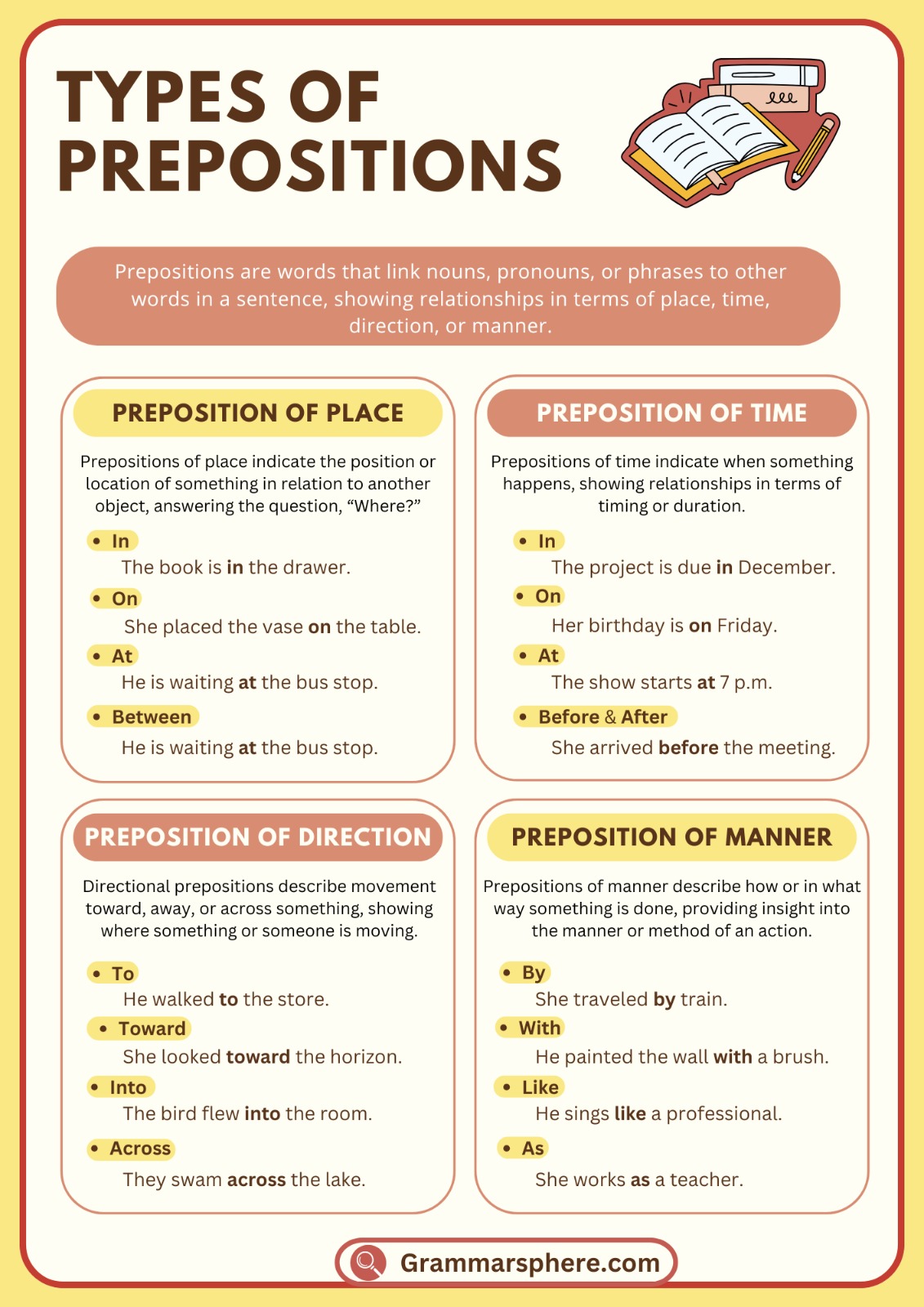
Types of Prepositions
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Direction
- Prepositions of Manner
- Prepositions of Agent or Instrument
- Prepositions of Possessions
- Prepositions of Cause or Purpose
- Prepositions of Comparison
- Prepositions of Condition
1. Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place show the location of something in relation to something else. Common examples are in, on, under, and between.
- The book is on the table.
- She stood between her friends.
- The cat under is the table.
2. Prepositions of Time
These prepositions indicate when something happens, often showing specific time frames. Common examples are at, in, and on.
- He arrived at 5 o’clock.
- We go to the beach in summer.
- Her birthday is on Monday.
3. Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction show movement toward or away from something. Examples include to, into, and through.
- She walked to the store.
- He climbed into the car.
- The bird flew through the window.
4. Prepositions of Manner
These prepositions describe the way or method something is done. Common ones are by and with.
- She solved the problem with patience.
- They traveled by train.
- He wrote the letter with a pen.
5. Prepositions of Agent or Instrument
These prepositions show a cause or who/what causes an action. Common ones are by and with.
- The book was written by the author.
- He cut the paper with scissors.
- The meeting was organized by the manager.
6. Prepositions of Possession
These prepositions show ownership or belonging. Common examples are of, with, and to.
- The keys of the car are missing.
- She is the girl with the red dress.
- The title to the house is with the owner.
7. Prepositions of Cause or Purpose
These prepositions indicate why something happens. Common examples include for and because of.
- They stayed home because of the rain.
- She works hard for her family.
- He apologized for his mistake.
8. Prepositions of Comparison
These prepositions help to compare two or more things. Common ones include like and as.
- He sings like a professional.
- She’s as tall as her brother.
- The lake is calm like a mirror.
9. Prepositions of Condition
These prepositions indicate the conditions under which something happens. Common examples are in case of and without.
- Take an umbrella in case of rain.
- He left without saying goodbye.
- They will call you in case of any changes.
When to Use Prepositions
Prepositions are essential for creating clear and specific sentences. They help link ideas and give important details about location, time, direction, and relationships. Here’s when to use prepositions:
1. Showing Location
Use prepositions to indicate where something is. They clarify the position or place of a person, object, or event in relation to something else.
- The keys are on the table.
- She stood beside her friend.
2. Indicating Time
Prepositions also specify when something happens, often giving details about dates, months, or specific times.
- The meeting is at 3 p.m.
- They travel in December.
3. Describing Movement or Direction
When you need to show movement toward a place or direction, prepositions clarify where something or someone is going.
- He walked to the store.
- The dog jumped into the car.
4. Explaining How Something is Done (Manner)
Prepositions can indicate the manner in which an action is done, showing how it happened.
- She spoke with confidence.
- He finished the task in a hurry.
5. Expressing Ownership or Belonging
To show possession or ownership, use prepositions that describe who owns or is connected to something.
- The cover of the book is red.
- She’s the girl with the blue hat.
6. Explaining Reason or Purpose
Prepositions can also explain why something is done, providing reasons or goals.
- He studied hard for the exam.
- They stayed indoors because of the rain.
Common Preposition Mistakes
1. Using the Wrong Preposition for Time or Place
Many learners mix up prepositions for time and place, like in, on, and at.
✓ He arrived at the airport on time.
✗ He arrived in the airport in time.
2. Adding Unnecessary Prepositions
Some sentences don’t need extra prepositions, but they’re added by mistake. Avoid adding prepositions when they’re not needed.
✓ Where did you go yesterday?
✗ Where did you go to yesterday?
3. Confusing Prepositions with Similar Meanings
Words like between and among or in and into often cause confusion.
✓ The discussion was between two friends.
✗ The discussion was among two friends.
4. Incorrectly Using Prepositions with Verbs
Some verbs have specific prepositions that must follow them. For example, “listen to” is correct, but “listen” alone can be incorrect.
✓ She listened to the teacher carefully.
✗ She listened the teacher carefully.
5. Overusing Prepositions
Sometimes, learners repeat or add unnecessary prepositions, which can make sentences awkward.
✓ She’s good at math.
✗ She’s good at in math.
Example Sentences with Prepositions
- She arrived at the station just in time.
- The book is on the top shelf.
- He walked through the forest to reach the lake.
- We met in the park yesterday.
- The keys are under the mat.
- They are traveling to France next month.
- The cat is hiding behind the curtain.
- She sits beside her best friend in class.
- He jumped into the pool with excitement.
- The meeting starts at 10 a.m. sharp.
- I found my notes between the pages of my textbook.
You May Also Like







Leave a Comment