Table of Contents
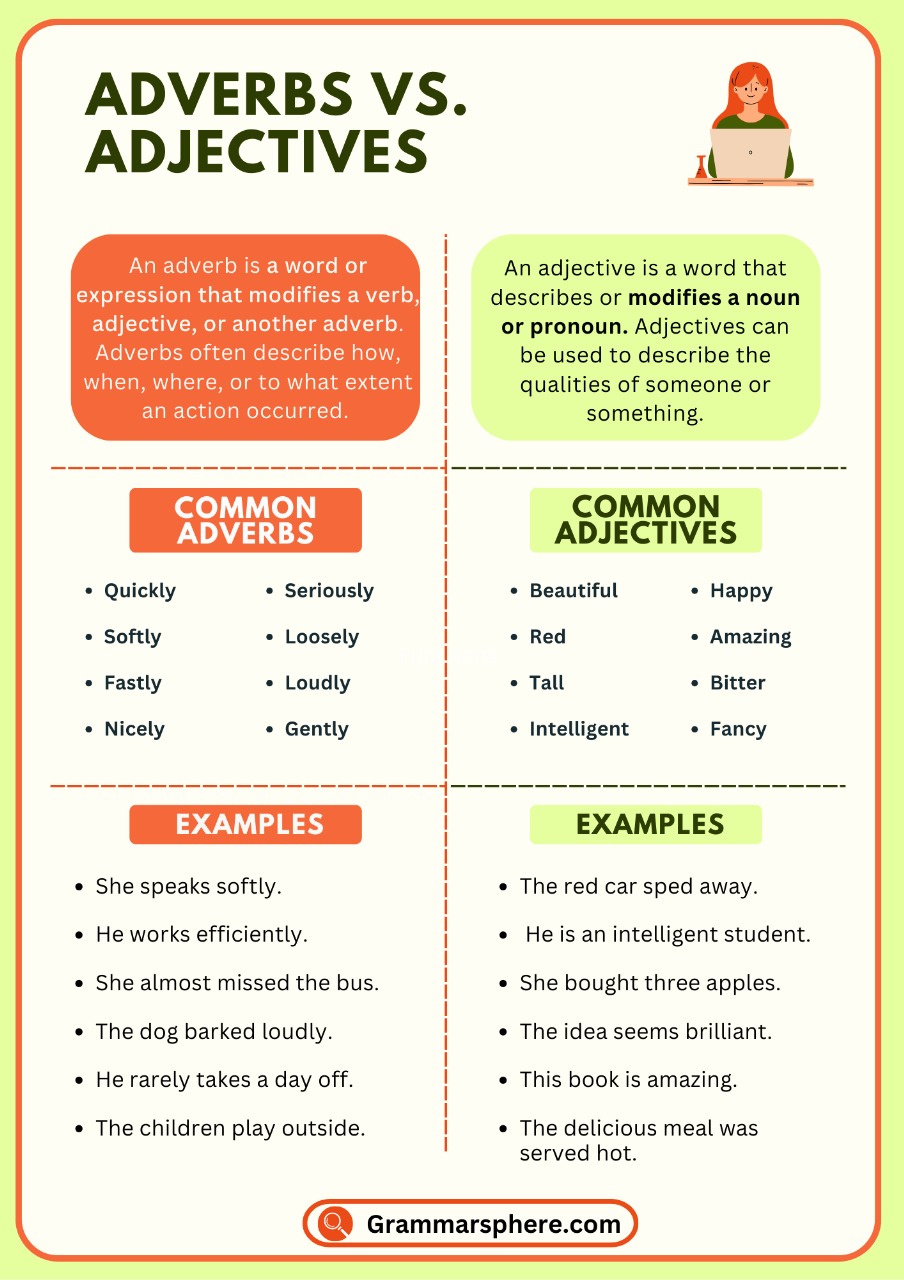
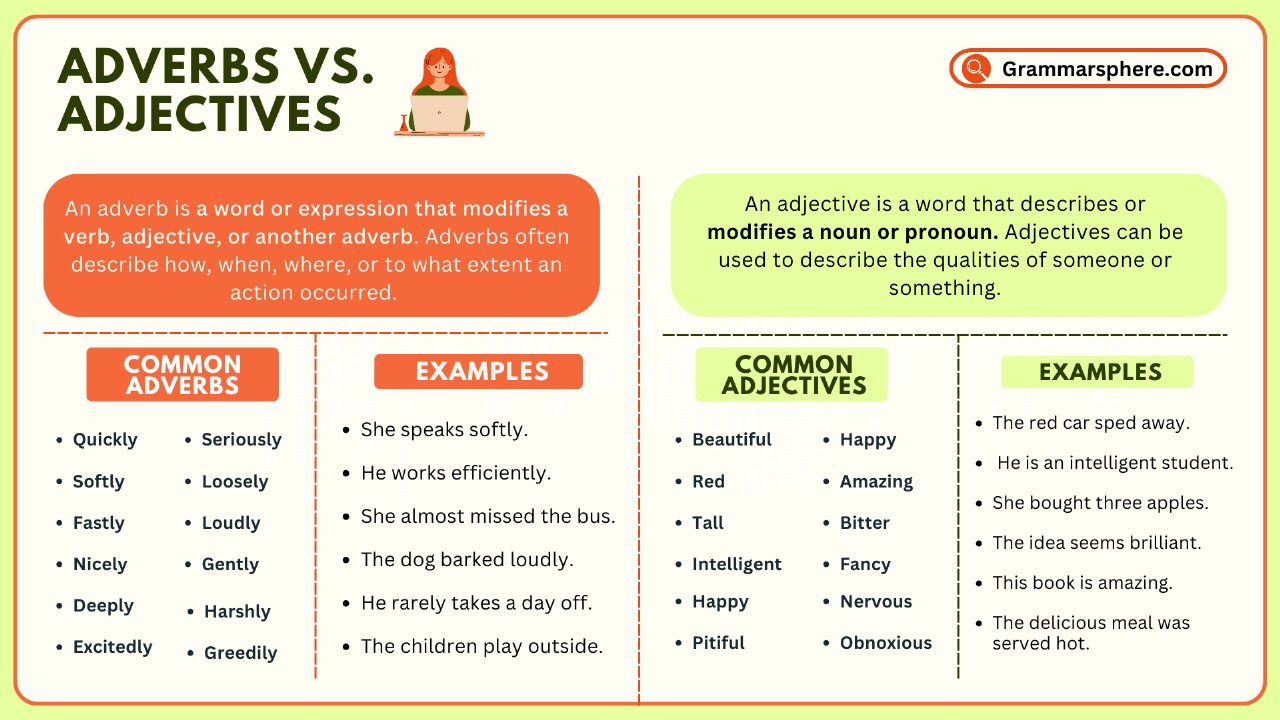
Adjectives and adverbs are words that help describe things in a sentence. Adjectives tell us more about nouns and pronouns, while adverbs give more details about verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
They help make sentences clearer by showing how something looks, feels, or happens. Learning adjectives and adverbs makes speaking and writing more interesting and easy to understand.
What is an Adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun by giving more information about its quality, quantity, size, shape, color, or condition.
Examples:
- The tall man walked into the room.
- She wore a beautiful dress to the party.
- The cold weather made everyone stay indoors.
Types of Adjectives
| Type of Adjective | Example |
|---|---|
| Descriptive Adjective | The blue sky looked beautiful. |
| Quantitative Adjective | She bought five apples. |
| Proper Adjective | I love Italian cuisine. |
| Demonstrative Adjective | This book is interesting. |
| Possessive Adjective | That is my car. |
| Interrogative Adjective | Which road should we take? |
| Comparative Adjective | This chair is more comfortable than that one. |
| Superlative Adjective | He is the tallest player on the team. |
| Predicate Adjective | The soup tastes delicious. |
What is an Adverb?
An adverb is a word that describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It tells us how, when, where, how much, or to what extent an action is performed.
Examples:
- She danced gracefully on the stage.
- The boy ran quickly to catch the bus.
- He spoke very softly during the meeting.
Types of Adverbs
| Type of Adverb | Example |
|---|
| Adverb of Manner | She sings beautifully. |
| Adverb of Time | We will leave tomorrow. |
| Adverb of Place | He looked everywhere for his keys. |
| Adverb of Frequency | She always reads before bed. |
| Adverb of Degree | The movie was extremely good. |
| Adverb of Certainty | He will definitely win the race. |
| Interrogative Adverb | When will the train arrive? |
| Relative Adverb | This is the house where I grew up. |
Difference Between Adjective and Adverb
Adjectives and adverbs can be tricky because they both describe other words, but they describe different types of words.
Adjectives
Adjectives describe nouns (people, places, or things) and give more information about them. For example:
- The tall tree
- A happy dog
Adjectives can also describe pronouns like “he,” “she,” or “it.”
Sometimes, several words can work together as a single unit to describe a noun. This is called an adjective phrase.
For example:
- The movie was too boring to watch.
Adverbs
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, or even other adverbs. They tell us more about an action, a quality, or the degree of something.
For example:
- She runs quickly (describes the verb “runs”).
- The room is very clean (describes the adjective “clean”).
- He spoke extremely softly (describes the adverb “softly”).
Adverbs often answer questions like how, when, where, or to what extent.
Key Differences
1. What They Describe
- Adjectives describe nouns or pronouns.
- Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
2. Usage Examples
- Adjective: The blue sky (describes the noun “sky”).
- Adverb: She sings beautifully (describes how she sings, a verb).
3. Common Clues
Adverbs often end in -ly, but not always. For example:
4. Intensity Modifiers
Adverbs can modify adjectives or other adverbs to show intensity:
- The food was very spicy (adverb “very” describes the adjective “spicy”).
- He ran quite slowly (adverb “quite” modifies the adverb “slowly”).
Adjectives and Adverbs in Sentences
| Adjective Sentence | Adverb Sentence |
|---|---|
| The happy child laughed. | The child laughed happily. |
| She is a quiet girl. | She speaks quietly. |
| The cake was delicious. | She baked the cake perfectly. |
| It was a fast car. | He drove the car fast. |
| The manager was rude. | The manager often speaks rudely. |
Common Adjectives and Adverbs
List of Adjectives
- Happy
- Quiet
- Delicious
- Fast
- Bright
- Rude
- Beautiful
- Calm
- Good
- Funny
- Cold
- Strong
- Tall
- Small
- Brave
- Angry
- Lazy
- Smart
- Elegant
- Friendly
List of adverbs
- Happily
- Quietly
- Perfectly
- Fast
- Brightly
- Rudely
- Beautifully
- Calmly
- Well
- Loudly
- Coldly
- Strongly
- Quickly
- Slowly
- Bravely
- Angrily
- Lazily
- Smartly
- Elegantly
- Politely
Adjective vs. Adverb: linking verbs
Linking verbs can make it tricky to decide whether to use an adjective or an adverb. Unlike action verbs that show what the subject is doing, linking verbs connect the subject to more information about it. They describe the subject’s state or condition rather than an action.
Common Linking Verbs
- The verb be (e.g., am, is, are, was, were)
- Verbs like become or seem
- Sensory verbs like look, feel, smell, sound, taste
When using linking verbs, whether to choose an adjective or an adverb depends on what you’re describing:
- Adjectives are used when describing the subject of the sentence.
- Adverbs are used when describing the action of the linking verb itself.
Examples to Understand the Difference
Adjective Example:
The soup tastes delicious.
Delicious is an adjective that describes the soup (the subject), not the action of tasting.
Adverb Example:
He tastes carefully while cooking.
Carefully is an adverb that describes the action of tasting (the verb).
Adjective Example:
She feels happy today.
The adjective happy explains her emotional state (the subject).
Adverb Example:
She feels deeply about her work.
The adverb deeply describes how she feels (the action).
How to Turn Adjectives into Adverbs
Many adjectives can be easily transformed into adverbs to describe actions or intensify other qualities. The process usually involves adding specific endings or making small changes to the adjective. Here’s how it works:
1. Adding “-ly”
For most adjectives, simply adding -ly to the end creates the adverb.
- Adjective → Adverb
- Loud → Loudly
- Perfect → Perfectly
- Hopeful → Hopefully
2. Adjectives Ending in “-y”
If the adjective ends in -y, replace the -y with -ily to make an adverb.
- Adjective → Adverb
- Easy → Easily
- Happy → Happily
- Lucky → Luckily
3. Adjectives Ending in “-le” or “-ble”
For adjectives ending in -le or -ble, remove the -e and replace it with -y to form the adverb.
- Adjective → Adverb
- Gentle → Gently
- Comfortable → Comfortably
- Terrible → Terribly
4. Adjectives Ending in “-ic”
If the adjective ends in -ic, add -ally to turn it into an adverb.
- Adjective → Adverb
- Specific → Specifically
- Tragic → Tragically
- Energetic → Energetically
Special Cases and Irregular Forms:
Not all adjectives follow these rules. Here are some exceptions:
1. Adjectives and adverbs that look the same:
Words like fast or hard can act as both adjectives and adverbs without any changes.
- He runs fast (adverb).
- It’s a fast car (adjective).
2. Adjectives ending in “-ly”:
Words like friendly, ugly, or silly don’t have typical adverb forms. Instead, you may need to rephrase the sentence or use a synonym:
Friendly → “in a friendly way” or “amicably”.
3. Irregular forms:
The adjective good has an irregular adverb form, well.
- She played well (adverb).
- She had a good game (adjective).
Common Mistakes with Adjectives and Adverbs
1. Using an Adjective When an Adverb Is Needed
❌ She sings in a friendly way.
✅ She sings beautifully.
2. Confusing Adjectives with Adverbs Ending in -ly
✅ She is a friendly singer.
❌ She sings friendly.
3. Using an Adverb to Modify a Noun
❌ She gave me a quickly response.
✅ She gave me a quick response.
4. Confusing “Well” with “Good”
✅ She played a good game last night.
❌ She played a well game last night.
5. Using “Bad” Instead of “Badly” After a Linking Verb
✅ The car smells bad.
❌ The car smells badly.
FAQS about Adverb and Adjective
What is the difference between an adverb, an adjective, and a verb?
Adjective: Describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
Example: The tall building touched the clouds.
Adverb: Describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
Example: She runs quickly in the race.
Verb: Shows an action, occurrence, or state of being.
Example: He jumps over the fence.
Adverb vs Adjective Examples
Adjective: The happy child laughed.
Adverb: The child laughed happily.
Adjective: It was a quiet night.
Adverb: She spoke quietly.
Adjective: The cake was delicious.
Adverb: She baked the cake perfectly.
Adjective: He is a fast runner.
Adverb: He ran fast.
Adjective: She is a careful driver.
Adverb: She drives carefully.
Can adverbs and adjectives be the same?
Yes, some words can function as both adjectives and adverbs, depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example:
Fast As an adjective: He drives a fast car.
As an adverb: He runs fast.
In such cases, the word’s function changes based on whether it is describing a noun (adjective) or a verb (adverb). However, not all words can do this, and most adjectives and adverbs have distinct forms.
How do you identify an adverb or adjective?
An adjective modifies a noun or pronoun and answers questions like “What kind?”, “Which one?”, or “How many?”.
Example: The tall building is impressive
An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb and answers questions like “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, or “To what extent?”.
Example: He works hard.
You May Also Like








Leave a Comment