Table of Contents
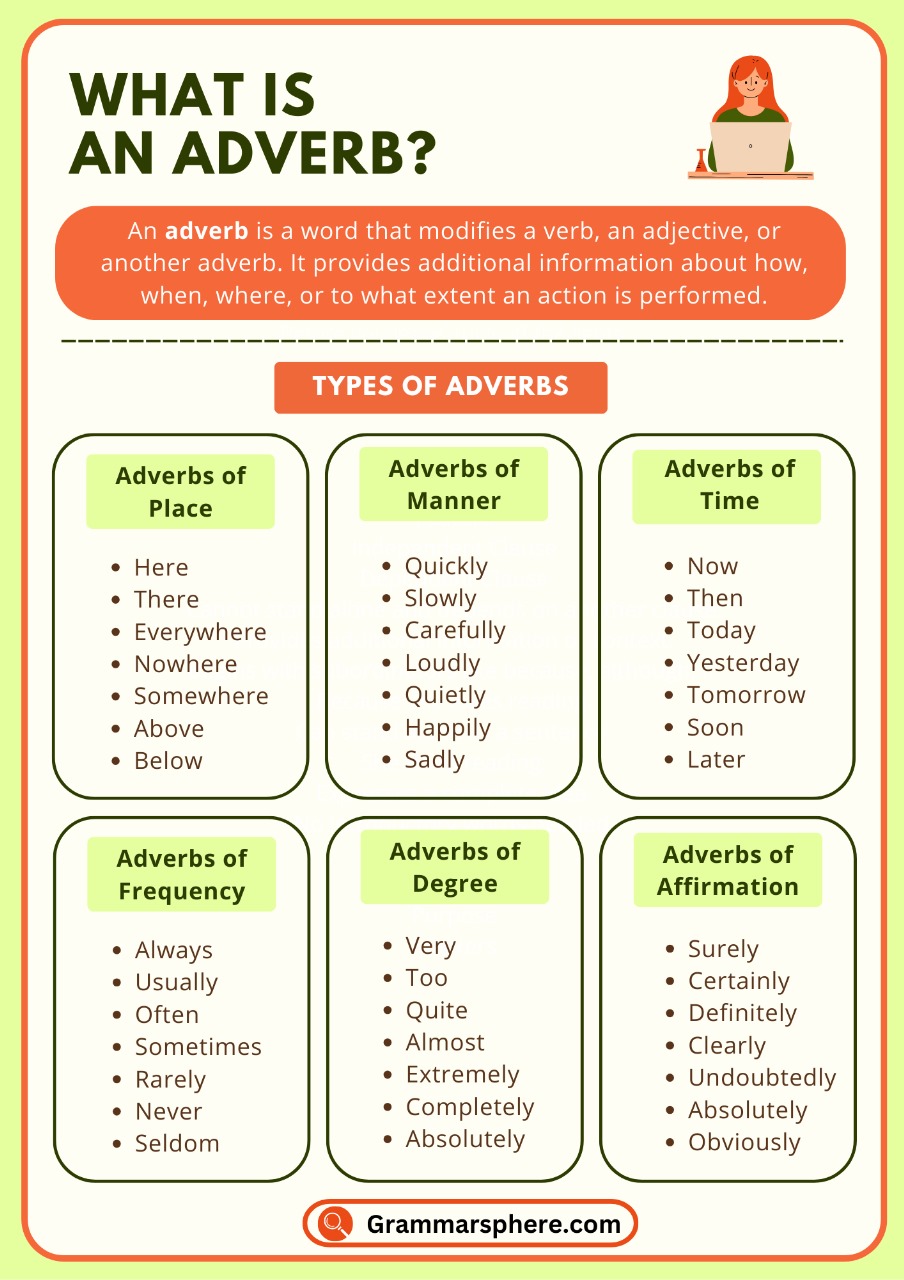
Adverbs are an essential part of English grammar. They describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more information about how, when, where, or to what degree something happens.
Understanding adverbs and their usage is crucial to improving both written and spoken English. This guide will help you learn about adverbs, their types, and how to use them correctly in everyday sentences.
Adverb Definition
An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb to show how, when, where, or how much something happens, making sentences more clear and detailed.
For example:
- She runs quickly. (How does she run? She runs quickly.)
- He is very tall. (How tall is he? He is very tall.)
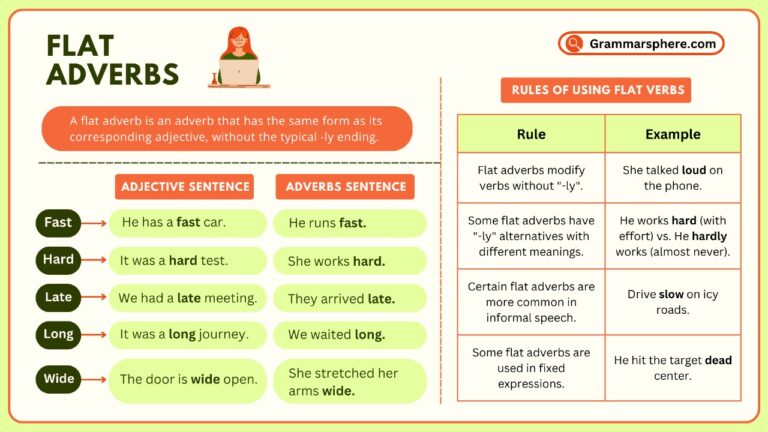
Flat Adverbs
Flat adverbs are adverbs that lack the -ly ending and remain in their base form. Despite this, they still modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Example of flat adverbs:
- She sings fast.
Here, fast is a flat adverb modifying the verb sings to describe how she sings. - He runs hard every day.
In this sentence, hard is a flat adverb modifying the verb runs and telling us how he runs.
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
Adverbs modify verbs by providing details on how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs, making sentences more informative and detailed.
For example:
- She sings beautifully.
- He studied hard.
Adverbs can also modify the meaning of a verb by describing its intensity or frequency, such as:
- He always helps others.
- She never arrives on time.
Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They answer the question How? and describe the manner or style of the verb’s action.
Examples of manner adverbs:
- Huan sings loudly in the shower.
- My cat waits impatiently for his food.
- I will seriously consider your suggestion.
Time
Adverbs of time tell us when an action occurs or how long it lasts. These adverbs help establish the timing or duration of an action.
Examples of time adverbs:
- We arrived at the theater and got in line early.
- Mara is confident that, eventually, her training will pay off.
- The weather will be cold and windy indefinitely.
Place
Adverbs of place describe where an action takes place. They answer the question Where? and give us information about the location of the action.
Examples of place adverbs:
- Turn in there, at the next left.
- Let’s go inside and ask how much they want for that guitar.
- The others hiked to the peak while she waited below.
Frequency
Adverbs of frequency describe how often an action occurs. They answer the question How often? and give information on the regularity of the verb’s action.
Examples of frequency adverbs:
- I used to go dancing regularly, but now I go only occasionally.
- Farid prefers to be paid monthly rather than weekly.
- Jun always eats lunch at the same time.
Degree
Adverbs of degree describe to what extent an action is done. They answer the question To what extent? and indicate the intensity or magnitude of the verb’s action.
Examples of degree adverbs:
- Have you fully read the instruction manual?
- It seems we’ve barely scratched the surface of this subject.
- The company is owned entirely by its workers.
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
Adverbs can also modify adjectives. When they do this, they provide more information about the quality or degree of the adjective they modify. These adverbs tell us how much, to what extent, or how intense something is.
For example:
- She is extremely talented.
Here, extremely is an adverb modifying the adjective talented, explaining the degree of her talent. - He is quite tall.
In this example, quite modifies the adjective tall to indicate the degree of height.
Common adverbs that modify adjectives include: very, extremely, quite, really, so, too.
Adverbs Modifying other Adverbs
Adverbs can also modify other adverbs, intensifying or altering their meaning. These adverbs answer questions about the degree or manner in which something happens.
For example:
- She sings incredibly well.
In this sentence, incredibly modifies the adverb well, showing to what degree she sings well. - He runs quite fast.
Here, quite modifies the adverb fast, giving more information about the speed at which he runs.
Adverbs and Sentences
Adverbs play a vital role in sentence structure, providing more detail and making the meaning of the action clearer. They can appear in different positions within a sentence depending on the type of adverb and the emphasis needed.
Examples:
- She always wakes up early. (Adverb of frequency placed at the beginning of the sentence for emphasis.)
- He completed his task quickly. (Adverb of manner placed after the verb.)
- We’ll meet tomorrow. (Adverb of time placed at the end of the sentence.)
Adverbs and Degrees of Comparison
Adverbs, like adjectives, can also express degrees of comparison. They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to show the intensity or comparison of an action, quality, or manner.
There are three degrees of comparison for adverbs:
| Degree of Comparison | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Degree | The adverb shows an action or condition without any comparison. | She dances gracefully. |
| Comparative Degree | The adverb compares two actions or conditions, often by adding -er or using more. | He runs faster than his friend. |
| Superlative Degree | The adverb shows the highest degree of an action or condition, often by adding -est or using most. | She sings most beautifully of all. |
Placement of Adverbs
Adverbs can be placed in various positions within a sentence, and their placement often depends on the type of adverb and the emphasis the speaker wants to give.
At the beginning of the sentence: Adverbs of frequency and time often appear here for emphasis.
- Never have I seen such beauty.
- Tomorrow, we will meet at the park.
In the middle of the sentence: Many adverbs of frequency and manner appear here, particularly between the subject and the verb, or after the auxiliary verb.
- She always arrives early.
- He has never visited that place.
At the end of the sentence: Adverbs of time and place are often placed here.
- She went to the store yesterday.
- They played outside today.
Common Adverb Mistakes to Avoid
Confusing Adverbs and Adjectives
Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Remember, adverbs answer how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
❌ She runs quick.
✔️ She runs quickly.
Misplacing Adverbs
Adverbs can be placed in various parts of a sentence, but incorrect placement can alter the meaning.
❌ She only speaks Spanish.
✔️ She speaks only Spanish.
Overuse of Adverbs
Overusing adverbs can weaken writing. Instead, focus on strong verbs and adjectives.
❌ She really wanted to go, but she really didn’t have time.
✔️ She was eager to go, but she didn’t have time.
Using Incorrect Adverbs for Comparison
When comparing actions, use the correct form of the adverb (comparative or superlative).
❌ She runs more faster than him.
✔️ She runs faster than him.
Conclusion
Adverbs are an essential part of English grammar, adding clarity and richness to sentences. By understanding how adverbs interact with verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs, you can improve your writing and speaking skills.
Always be mindful of their placement in sentences and avoid common mistakes like confusing adverbs with adjectives. With practice, you’ll use adverbs naturally and effectively to communicate your thoughts more clearly.
FAQs
What are adverbs and examples?
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb by giving more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
Examples of Adverbs:
Manner (How?) → She sings beautifully.
Time (When?) → We will meet tomorrow.
Place (Where?) → He looked everywhere.
Degree (To what extent?) → I am very tired.
What are the 4 types of adverbs?
Adverbs of Manner (How?) → She ran quickly.
Adverbs of Time (When?) → They arrived yesterday.
Adverbs of Place (Where?) → He looked outside.
Adverbs of Degree (To what extent?) → She is very happy.
What are 15 adverbs?
Quickly, carefully, loudly, gently, happily, regretfully, softly, suddenly, rapidly, barely, cautiously, silently, sharply, calmly, safely.
You May Also Like







Leave a Comment