Table of Contents
Adjectives help us describe things, people, or places. But what happens when we need to compare one thing to another, or even among many? That’s where comparative and superlative adjectives come into play.
Mastering comparative and superlative adjectives is essential for improving both written and spoken English. Whether you’re writing an essay, delivering a presentation, or engaging in casual conversation, knowing how to properly compare and contrast things can make your communication clearer and more effective.
What Are Comparative Adjectives?
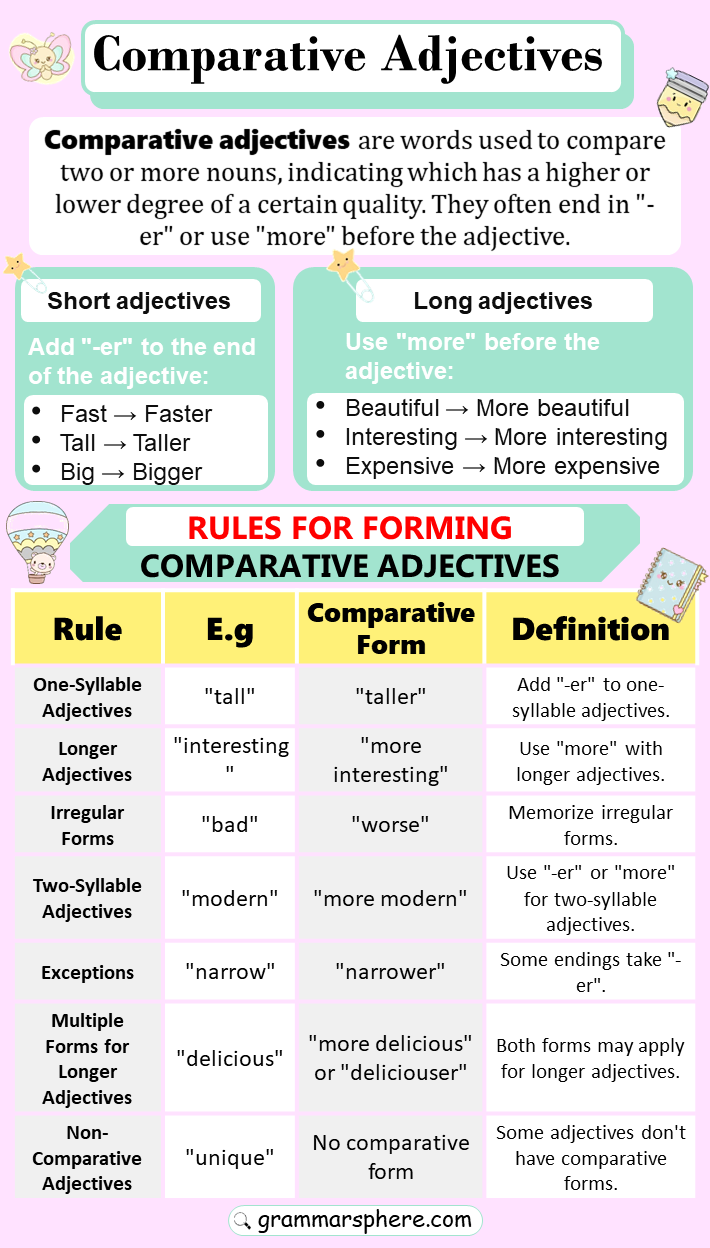
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two things. They help us describe differences by showing whether one thing is larger, smaller, faster, slower, or has some other quality in a greater or lesser degree than the other.
Example Sentences:
This book is larger than that one I bought last week.
My cat is faster than my dog when they race to the food bowl.
Her house is smaller than mine, but it’s more charming.
How to Form Comparative Adjectives
| Type of Adjective | Rule | Example |
|---|---|---|
| One-syllable adjectives | Add -er to the end | fast → faster, small → smaller |
| Two syllables ending in -y | Change -y to -ier | happy → happier, angry → angrier |
| Two or more syllables | Use more before the adjective | beautiful → more beautiful, difficult → more difficult |
| Irregular adjectives | No specific rule, irregular form | good → better, bad → worse |
How Irregular Adjectives are Formed?
Irregular adjectives do not follow the typical patterns for forming comparatives and superlatives. These forms need to be memorized.
For example: ‘good‘ becomes ‘better‘ in the comparative form and ‘best’ in the superlative form. Similarly, ‘bad’ changes to ‘worse‘ and ‘worst. , such as:
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|
| good | better | best |
| bad | worse | worst |
| far | farther / further | farthest / furthest |
| little | less | least |
| much | more | most |
| many | more | most |
| old | older / elder | oldest / eldest |
| late | later | latest |
| near | nearer / closer | nearest / closest |
| wise | wiser | wisest |
Comparative Adjectives in Sentences
- The red dress is prettier than the blue one.
- This test is harder than the last one we took.
- This movie is more exciting than the one we watched last week.
- Her explanation was clearer than his, so I understood it better.
What Are Superlative Adjectives?
superlative adjectives are used when you want to compare three or more things to show which one is the most or least in a group.
Example Sentences:
This is the most exciting game I have ever played.
She is the smartest student in the class.
This is the least expensive option available.
How to Form Superlative Adjectives?
| Type of Adjective | Rule | Example |
|---|
| One-syllable adjectives | Add -est to the end of the word | small → smallest, fast → fastest |
| Two syllables ending in -y | Change -y to -iest | happy → happiest, angry → angriest |
| Two or more syllables | Use most or least before the adjective | beautiful → most beautiful, difficult → most difficult |
| Irregular adjectives | No specific rule, irregular form | good → best, bad → worst |
irregular Superlative Form
Irregular superlatives are adjectives that do not follow the standard rules for forming comparatives and superlatives. Instead, they have unique forms that must be memorized.
These adjectives change significantly in their comparative and superlative forms, differing from the typical -er and –est pattern.
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| good | better | best |
| bad | worse | worst |
| far | farther / further | farthest / furthest |
| little | less | least |
| much | more | most |
Superlative Adjectives in Sentences
- She is the most talented singer in the competition.
- This is the best restaurant I’ve ever been to.
- This is the most interesting book I’ve ever read.
- He is the fastest runner on the track team.
Rules for Using Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
1. One-Syllable Adjectives
For one-syllable adjectives, form the comparative by adding –er and the superlative by adding -est.
- tall → taller
- tall → tallest
2. Two-Syllable Adjectives Ending in -y
For two-syllable adjectives ending in –y, change the y to i and add –er for comparatives, and add –est for superlatives.
- happy → happier
- happy → happiest
Below is a table that explains the rule with examples of how to form comparative and superlative adjectives for both regular and exceptions (doubling the consonant):
| Adjective | Rule | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|---|
| thin | Add -er for comparative, -est for superlative | thinner | thinnest |
| fast | Add -er for comparative, -est for superlative | faster | fastest |
| cold | Add -er for comparative, -est for superlative | colder | coldest |
| big | Double the final consonant and add -er/-est | bigger | biggest |
| hot | Double the final consonant and add -er/-est | hotter | hottest |
| sad | Double the final consonant and add -er/-est | sadder | saddest |
Explanation:
Regular adjectives
(like thin, fast, and cold) simply add -er for the comparative and -est for the superlative.
Exception rule:
If an adjective ends in a single consonant preceded by a single vowel, you double the final consonant before adding -er or -est (e.g., big becomes bigger and biggest).
3. Two-Syllable Adjectives Not Ending in -y
For two-syllable adjectives that do not end in –y, use more for comparatives and 1 for superlatives.
- careful → more careful
- careful → the most careful
4. Three or More Syllable Adjectives
For adjectives with three or more syllables, use more for comparatives and the most for superlatives.
- intelligent → more intelligent
- intelligent → the most intelligent
5. Irregular Adjectives
Some adjectives have irregular forms for comparatives and superlatives and do not follow the standard rules.
- Good → better (comparative), best (superlative)
- Bad → worse (comparative), worst (superlative)
Differences Between Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
1. Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare two people, places, things, or ideas. They often end in –er or are preceded by more.
How to Form:
For one-syllable adjectives, add –er to the end of the adjective. For adjectives with two or more syllables, use more before the adjective.
Examples:
- John is taller than Mark.
- This book is more interesting than that one.
- My car is faster than your car.
2. Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives compare three or more people, places, things, or ideas. They usually end in –est or are preceded by “the most.
How to Form:
For one-syllable adjectives, add –est to the end of the adjective. For adjectives with two or more syllables, use the most before the adjective.
Examples:
- John is the tallest in the class.
- This is the most interesting book I’ve ever read.
- She is the fastest runner on the team.
FAQS:
1. Q: Can a word be both comparative and superlative?
A: Yes! Words like ‘fast’ can be used in both comparative (‘faster’) and superlative (‘fastest’) forms.
2. Q: When should I use “more” and “most” for comparatives and superlatives?
A: Use “more” for adjectives with two or more syllables (except those ending in -y, where you add -ier). For superlatives, use “most” for adjectives with two or more syllables.
Example:
Comparative: more beautiful, more difficult
Superlative: most beautiful, most difficult
3. Q: What is the difference between “older” and “elder”?
A: “Older” is used to compare age in general, while “elder” is often used when talking about family members.
Example:
My sister is older than me.
My elder brother helped me with my homework.
4. Q: Can irregular adjectives be used in both comparative and superlative forms?
A: Yes, irregular adjectives like “good,” “bad,” “far,” etc., have unique comparative and superlative forms.
Example:
Good → better (comparative), best (superlative)
Bad → worse (comparative), worst (superlative)
5. Q: Can adjectives with more than two syllables have regular comparative and superlative forms?
A: No, adjectives with more than two syllables typically do not follow the regular pattern of adding “-er” or “-est”. Instead, you use “more” for the comparative and “most” for the superlative.
Example:
Comparative: more intelligent, more beautiful
Superlative: most intelligent, most beautiful
You May Also Like








Leave a Comment