Table of Contents
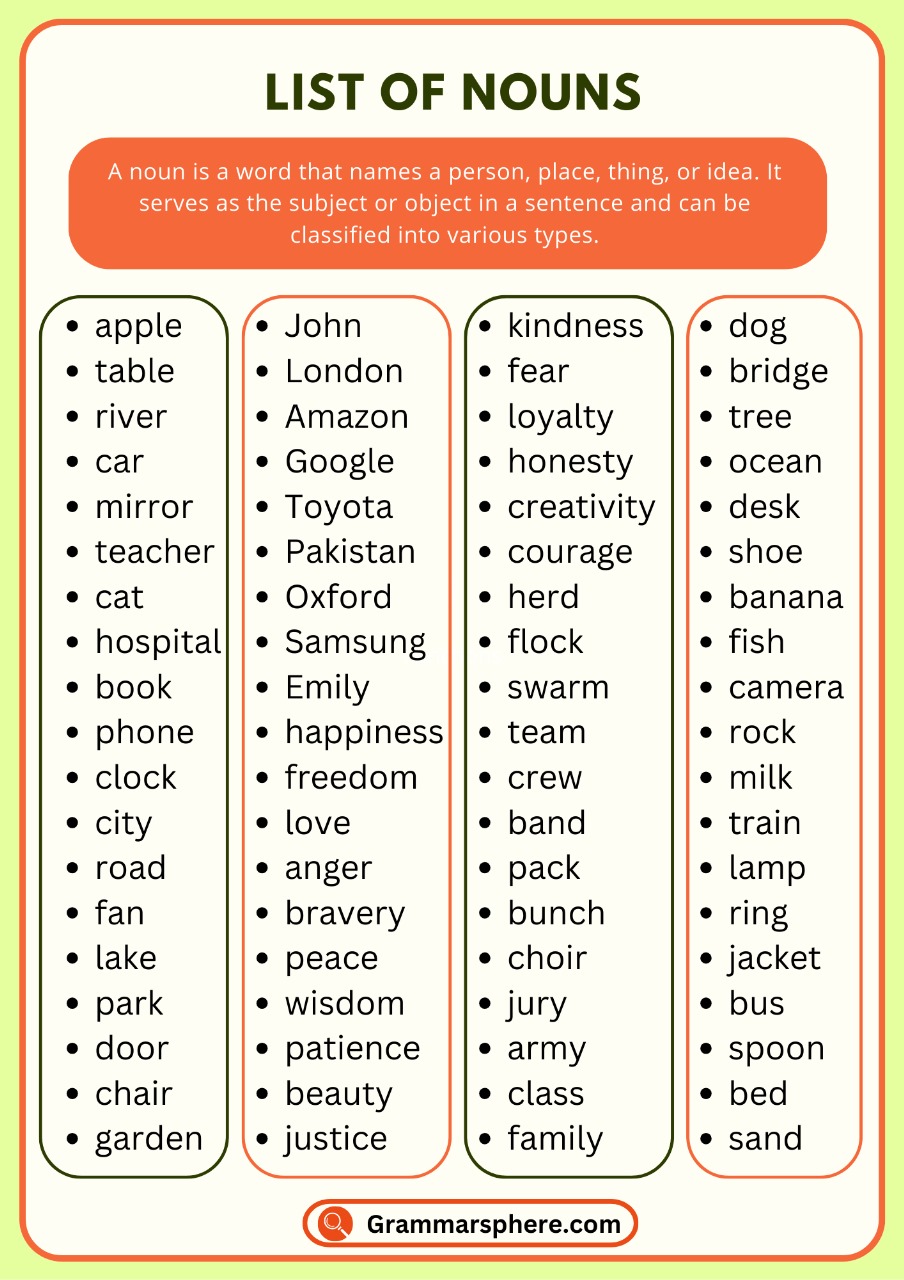
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They are essential in forming sentences and help us describe the world around us. There are different types of nouns, including proper, common, abstract, concrete, and collective nouns. Each type has a unique role in communication.
What is a Noun?

A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
Examples of Nouns:
People: teacher, doctor, John, Emily
Places: school, city, London, park
Things: book, table, computer, car
Ideas: love, happiness, freedom, justice
Types of Nouns
1. Proper Nouns
These nouns name specific people, places, or organizations and always begin with a capital letter.
- Albert Einstein
- Paris
2. Common Nouns
These refer to general people, places, or things rather than specific ones.
- teacher
- country
- phone
3. Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns refer to things that can be touched, seen, heard, tasted, or smelled.
- apple (can be tasted)
- music (can be heard)
- tree (can be seen and touched)
4. Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, or states of being that cannot be physically sensed.
- bravery
- love
- intelligence
5. Collective Nouns
These nouns refer to a group of people or things as a single entity.
- team
- flock
- jury
6. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are things that can be counted (singular or plural).
- apple → apples
- book → books
7. Uncountable Nouns
These refer to substances or concepts that cannot be counted individually.
- water
- sugar
- happiness
8. Possessive Nouns
These indicate ownership or possession.
- John’s book
- The cat’s tail
Function of a Noun in a Sentence
Nouns serve various grammatical roles in a sentence. Here are some of their main functions:
1. Subject
The noun performs the action in a sentence.
- The dog barks loudly.
2. Object
The noun receives the action of a verb.
- She reads a book.
3. Predicate Noun
A noun that follows a linking verb and renames the subject.
- He is a doctor.
4. Possessive Noun
Shows ownership.
- This is Emma’s pen.
5. Object of a Preposition
Comes after a preposition in a phrase.
- She sat on the chair.
List of Nouns in English
| Apple | River | Chair | Love | Team |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dog | London | Freedom | Gold | School |
| Car | Happiness | Mountain | Family | Computer |
| Book | Microsoft | Justice | Plastic | Ocean |
| House | Honesty | Wood | Choir | Elephant |
| Table | Amazon | Tree | Iron | Army |
| Water | Fear | Pack | Steel | Library |
| Success | Swarm | Diamond | City | |
| Kindness | Shakespeare | Team | Leather | Tower |
| Intelligence | Tesla | Audience | Cotton | Garden |
| Lake | Castle | Friend | Victory | Pencil |
| Jacket | Rainbow | Courage | Patience | Light |
| Thunder | Window | Dictionary | Bicycle | Bridge |
| Science | Village | Helicopter | Bakery | Island |
| Thunderstorm | Telescope | Traffic | Calendar | Statue |
| Festival | Universe | Strategy | Melody | Teacher |
| Volcano | Invention | Planet | Sculpture | Desert |
| Grammar | Necklace | Adventure | Dictionary | Stadium |
| Clock | Perfume | Mystery | Garden | Market |
| Rocket | Orchestra | Puzzle | Telescope | Moon |
| Competition | Notebook | Electricity | Umbrella | Blanket |
| Satellite | Carnival | Magazine | Culture | Castle |
| Encyclopedia | Physics | Chemistry | Sculpture | Celebration |
| Fountain | Treasure | Rainbow | Octopus | Sunglasses |
| Artwork | Museum | Jungle | Detective | Farmer |
| Dinosaur | Lighthouse | Recipe | Parliament | Acrobat |
| Backpack | Tournament | Galaxy | Solar System | Waterfall |
| Secretary | Postcard | Detective | Highway | Scientist |
| Mathematician | Submarine | Conductor | Orchestra | Blueprint |
| Engineer | Typing | Collection | Donation | Volunteer |
| Elevator | Compass | Canyon | Sculpture | Aquarium |
| Stopwatch | Landscape | Castle | Announcement | Parliament |
| Gymnasium | Manuscript | Blizzard | Professor | Intersection |
| Biography | Ballet | Lighthouse | Journey | Eclipse |
| Marketplace | Seashore | Observatory | Philosophy | Experiment |
| Campaign | Billboard | Hieroglyph | Bookmark | Landmark |
| Cathedral | Sculpture | Eruption | Universe | Archaeology |
| Agriculture | Kaleidoscope | Observatory | Synchronization | Civilization |
| Architecture | Celebration | Astronomy | Encyclopedia | Legislature |
| Summit | Cartography | Memorandum | Synchronization | Boulevard |
| Avalanche | Sanctuary | Renaissance | Parliament | Amphitheater |
| Industrialization | Constellation | Innovation | Teleportation | Investigation |
| Handwriting | Summit | Cartography | Synchronization | Blueprint |
| Cartography | Boulevard | Memorandum | Synchronization | Legislation |
| Avalanche | Sanctuary | Renaissance | Parliament | Amphitheater |
| Telecommunication | Machinery | Citizenship | Conservation | Refinery |
| Negotiation | Philosophy | Migration | Capitalism | Administration |
| Astronomy | Acrobatics | Architecture | Anthropology | Cinematography |
| Literature | Mythology | Meteorology | Linguistics | Journalism |
| Industrialization | Navigation | Synchronization | Coordination | Conservation |
| Refinery | Revolution | Transportation | Civilization | Parliament |
| Electricity | Machinery | Technology | Archaeology | Experimentation |
| Sociology | Agriculture | Illustration | Mathematics | Investigation |
| Preservation | Exploration | Acceleration | Engineering | Restoration |
| Colonization | Manufacturing | Urbanization | Communication | Construction |
| Transportation | Synchronization | Telecommunication | Entrepreneurship | Innovation |
FAQs About Nouns
1. What is a noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea.
Examples: teacher, park, book, happiness.
2. What are the main types of nouns?
Nouns can be proper, common, concrete, abstract, collective, countable, and uncountable.
Examples:
Proper: London, Tesla
Common: city, company
Concrete: chair, apple
Abstract: love, bravery
Collective: team, flock
3. What are countable and uncountable nouns?
Countable nouns can be counted (e.g., apple, car, book).
Uncountable nouns cannot be counted individually (e.g., water, rice, happiness).
4. What is a collective noun?
A collective noun refers to a group of things or people as one unit.
Examples: team, herd, family, jury.
5. How do nouns function in sentences?
Nouns act as subjects, objects, predicate nouns, and objects of prepositions.
Example:
Subject: The dog barks.
Object: She reads a book.
Possessive: This is John’s phone.
You May Also Like









Leave a Comment