Table of Contents
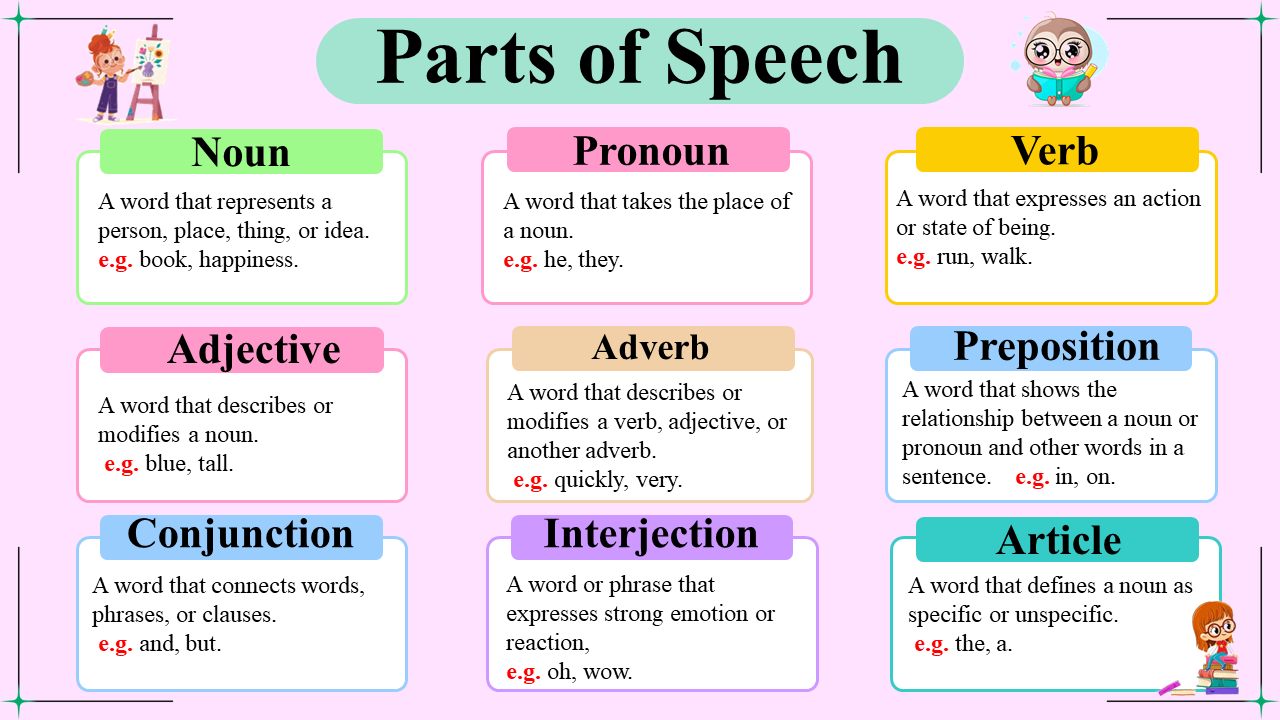
One of the basic fundamentals of the English language is the understanding of parts of speech. Categories of words are subdivided according to their usage in a certain sentence, known as parts of speech. With this knowledge, you can fine-tune what each part of speech will do for you and thus make your written and spoken word intelligently constructed English.
Nouns:
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They are the subjects and objects in sentences, making them a crucial part of speech.
Types of Nouns
- Proper Nouns: These are specific names of people, places, or things, such as John, Paris, or Google.
- Common Nouns: General names for people, places, or things like man, city, or company.
- Abstract Nouns: Words that name ideas, feelings, or qualities, such as love, freedom, or happiness.
- Concrete Nouns: Names for things you can see, touch, hear, smell, or taste, like book, apple, or music.
- Countable Nouns: Nouns that can be counted, such as car (one car, two cars).
- Uncountable Nouns: Nouns that cannot be counted, like water or sand.
- Collective Nouns: Words that name a group of people or things, such as team or flock.
- Compound Nouns: Nouns made up of two or more words, like toothpaste or mother-in-law.
Examples of Nouns in Sentences
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
- She traveled to London last summer.
- His happiness was evident after he received the news.
- The car is parked in the garage.
- We need more information to make a decision.
Nouns are essential in sentences because they provide the names of the people, places, things, or ideas being discussed.
Pronouns:
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in sentences, helping to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother.
Types of Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns: Words like he, she, it, they.
- Possessive Pronouns: Words like my, your, his, her.
- Reflexive Pronouns: Words like myself, yourself.
- Relative Pronouns: Words like who, which, that.
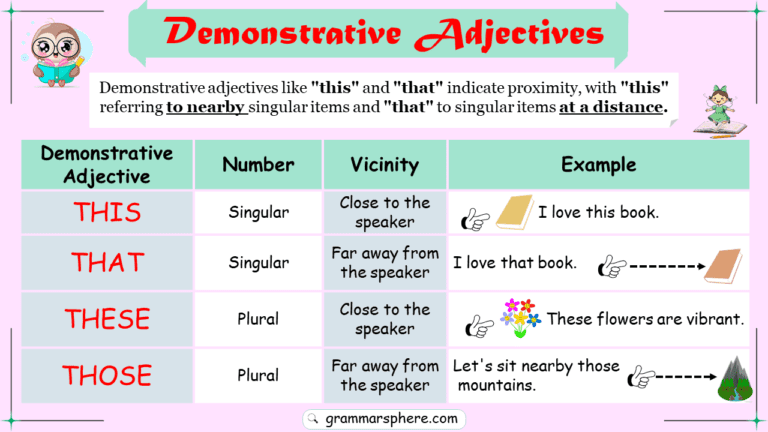
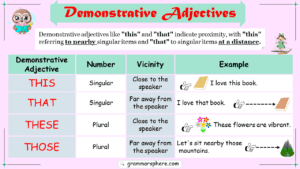
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Words like this, that, these, those.
- Interrogative Pronouns: Words like who, what, which.
- Indefinite Pronouns: Words like someone, anybody, each.
- Reciprocal Pronouns: Words like each other, one another.
Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
- She loves to read books.
- They are planning a trip to the mountains.
- It is a sunny day today.
- We should help each other in times of need.
- Who is calling me at this hour?
Pronouns are used to replace nouns in a sentence, making the sentence less repetitive and more fluid.
Verbs:
Verbs are action words that describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. They can also express states of being.
Types of Verbs
- Action Verbs: Words that describe physical or mental actions, such as run, think, write.
- Linking Verbs: Words that connect the subject to more information, like is, seem.
- Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs: Words like be, do, have that help form tenses.
- Modal Verbs: Words like can, might, will that express ability, possibility, or necessity.
- Transitive Verbs: Verbs that require an object, like buy, see.
- Intransitive Verbs: Verbs that do not require an object, like sleep, arrive.
- Phrasal Verbs: Verbs combined with prepositions or adverbs to create a new meaning, like give up, look after.
Verb Tenses
- Present Tense: She writes every day.
- Past Tense: He walked to the store yesterday.
- Future Tense: They will travel to Japan next year.
- Present Perfect: I have finished my homework.
- Past Perfect: She had left before I arrived.
- Future Perfect: We will have completed the project by tomorrow.
Examples of Verbs in Sentences
- She runs every morning.
- They are preparing for the exam.
- He seems very happy today.
- The baby cries a lot at night.
- We will go to the movies tomorrow.
Verbs are the heart of a sentence, telling us what the subject is doing or being.
Adjectives:
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns and pronouns, providing more details about them.
Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives: Words that describe qualities, such as beautiful, tall, short.
- Quantitative Adjectives: Words that describe quantity, like many, few, several.
- Demonstrative Adjectives: Words like this, that, these, those.
- Possessive Adjectives: Words like my, your, his.
- Interrogative Adjectives: Words like which, what, whose.
- Comparative and Superlative Adjectives: Smarter, the smartest.
- Articles: The (definite article) and a, an (indefinite articles).
Adjective Order
Adjectives in English often follow a specific order when multiple adjectives are used. The usual order is: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose (e.g., a beautiful, large, old, round, brown, Italian, leather sofa).
Examples of Adjectives in Sentences
- She wore a red dress to the party.
- It was a cold winter morning.
- The large dog barked loudly.
- We live in a small apartment.
- He gave me a long explanation.
Adjectives help us to provide specific details and paint a clearer picture of the noun or pronoun being described.
Adverbs:
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more details about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
Types of Adverbs
- Adverbs of Manner: Quickly, slowly.
- Adverbs of Place: Here, there.
- Adverbs of Time: Now, later.
- Adverbs of Frequency: Always, never.
- Adverbs of Degree: Very, quite.
- Adverbs of Reason: Therefore, thus.
- Interrogative Adverbs: How, when, why.
Examples of Adverbs in Sentences
- She runs quickly in the mornings.
- They arrived yesterday.
- He speaks very clearly.
- We will leave soon.
- The baby cried loudly.
Adverbs are essential for adding details and giving more context to the actions, qualities, or other adverbs in a sentence.
Prepositions:
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence, often indicating time, place, or direction.
Types of Prepositions
- Prepositions of Time: At, on, in.
- Prepositions of Place: Under, over, between.
- Prepositions of Direction: To, towards, from.
- Prepositions of Agent: By, with.
- Prepositions of Instrument: With, by.
- Complex Prepositions: In front of, on top of.
Prepositional Phrases
Prepositions often form phrases with nouns, providing additional details about the subject. For example, “The cat is on the mat.”
Examples of Prepositions in Sentences
- The book is on the table.
- She went to the store.
- We are going with them.
- The cat is hiding under the bed.
- They arrived after dinner.
Prepositions are important for showing relationships between different elements in a sentence.
Conjunctions:
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses, making sentences smoother and more coherent.
Types of Conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions: For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (FANBOYS).
- Subordinating Conjunctions: Because, although, since.
- Correlative Conjunctions: Either/or, neither/nor, both/and.
- Conjunctive Adverbs: However, therefore, moreover.
Examples of Conjunctions in Sentences
- She likes tea and coffee.
- He was tired, but he went to work.
- You can have cake or ice cream.
- We stayed home because it was raining.
- I am hungry, so I will eat.
Conjunctions are crucial for linking different parts of a sentence, ensuring the sentence flows smoothly.
Interjections:
Interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotion or reaction. They are often followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of Interjections in Sentences
- Wow! That’s amazing!
- Oh no! I forgot my keys.
- Oops! I made a mistake.
- Hey! Watch out!
- Yay! We won the game.
Interjections add emotion and excitement to sentences, helping to convey the speaker’s feelings.
Sentence Examples for the 9 Parts of Speech
Noun: : The dog is barking loudly.
Pronoun : They are going to the park.
Verb: She runs every morning.
Adverb: He sings beautifully.
Adjective: It was a bright day.
Preposition: The book is on the table.
Conjunction: I wanted to go, but it was raining.
Interjection: Wow! That’s amazing!
Article: The cat is sleeping.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of speech is key to mastering English. Each part of speech plays a unique role in sentence structure, allowing us to communicate clearly and effectively.
Whether you are just starting to learn English or looking to deepen your understanding, mastering the parts of speech is an essential step in your language journey. Keep practicing, and soon, using these parts of speech will become second nature to you.
You May Also Like








Leave a Comment