Table of Contents
Many learners struggle with the past continuous tense because it describes ongoing actions in the past. When should you use was or were? How does it differ from the simple past tense? This blog post helps learn past continuous tense with clear rules, structure, and examples. By mastering this tense, you’ll be able to describe past events in progress more accurately.
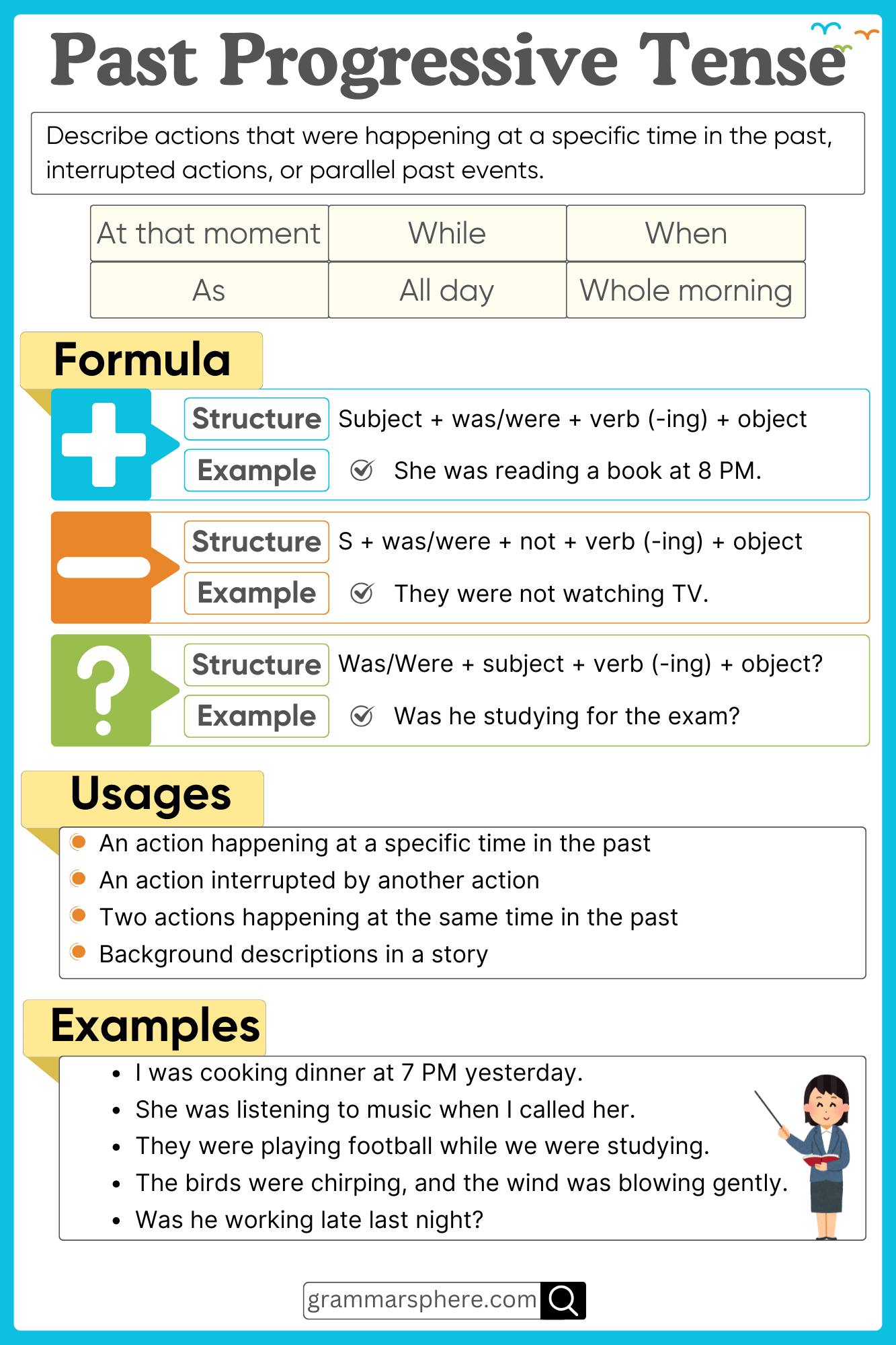
What is Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense describes actions that were ongoing at a specific moment in the past. It is often used to show interruptions, background activities, or simultaneous events.
Structure of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense is formed using: Subject + was/were + verb(-ing)
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha was reading a book when the phone rang.
- They were playing football in the park.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + not + verb(-ing) + object
- Aisha was not reading a book when the phone rang.
- They were not playing football in the park.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Was/Were + subject + verb(-ing) + object?
- Was Aisha reading a book when the phone rang?
- Were they playing football in the park?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + was/were + subject + verb(-ing) + object?
- What was Aisha reading when the phone rang?
- Why were they playing football in the park?
Subject-Verb Agreement
The helping verb was/were depends on the subject:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
| I/He/She/It | was |
| We/You/They | were |
Time Expressions in Past Continuous Tense
Common time expressions used with the Past Continuous Tense:
- At that moment: I was studying at that moment.
- While: She was cooking while I was cleaning.
- When: They were sleeping when the alarm rang.
- All day/night: We were working all day.
Adverb Placement in Past Continuous Tense
1. Before the main verb
(was/were + adverb + verb-ing) → Used for frequency or certainty.
- She was always studying late at night.
- He was constantly complaining.
2. After the object
Used for manner (how the action was performed).
- They were playing football seriously.
- She was writing her essay carefully.
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
1. Actions happening at a specific time in the past
Describes an action that was in progress at a particular moment.
- Ahmed was watching TV at 8 PM.
- They were playing football in the park at noon.
2. Actions interrupted by another action
Shows an ongoing action that was stopped by a sudden event.
- I was writing when my friend called.
- She was sleeping when the alarm rang.
3. Parallel actions
Describes two actions happening at the same time.
- While Maria was cooking, Ahmed was setting the table.
- The children were playing while their parents were talking.
4. Describing the background of a story
Sets the scene with ongoing actions in past narratives.
- The sun was shining, and the birds were singing.
- The wind was blowing, and people were rushing home.
Past Continuous vs. Future Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Past Continuous | Future Continuous |
| Definition | Describes an action that was happening at a specific time in the past. | Describes an action that will be happening at a specific time in the future. |
| Formula | Subject + was/were + V1 + ing + object | Subject + will be + V1 + ing + object |
| Usage | 1. Used for ongoing past actions. 2. Used for interrupted past actions. | 1. Used for ongoing future actions. 2. Used for parallel future actions. |
| Example Sentences | Malaika was studying at 8 PM. They were playing when it started to rain. | Malaika will be studying at 8 PM. They will be playing football tomorrow evening. |
Examples of the Past Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Aisha was reading a book when her friend called.
- They were playing football while it was raining.
- He was fixing his car when I saw him.
- We were having lunch when the power went out.
- The children were drawing pictures in class.
Negative:
- Sara was not paying attention during the meeting.
- We were not traveling last weekend.
- He was not feeling well in the morning.
- The baby was not crying when I checked.
- I was not using my phone when you texted.
Interrogative:
- Was she cooking when you arrived?
- Were they studying at the library?
- Was Ahmed working late last night?
- Were you sleeping when the storm started?
- Was the teacher explaining the topic clearly?
Common Mistakes with the Past Continuous Tense
1. Using the Base Form Instead of the -ing Form
❌ He was play football when it started raining.
✅ He was playing football when it started raining.
2. Using the Base Form Instead of the Present Participle
❌ We were finish our homework when the power went out.
✅ We were finishing our homework when the power went out.
3. Using the Past Simple Instead of the Past Continuous
❌ She was lived in London at that time.
✅ She was living in London at that time.
FAQs
When do we use the Past Continuous Tense?
We use it for ongoing past actions, interrupted actions, and background descriptions.
What is the difference between Simple Past and Past Continuous?
Simple Past focuses on completed actions, while Past Continuous emphasizes the duration of an action in the past.
Can we use stative verbs in Past Continuous?
No, verbs like know, believe, love, hate are not used in this tense.
Read More




Leave a Comment