Table of Contents
Many learners find the past perfect tense confusing because it describes actions completed before another past event. When should you use “had” + past participle? How does it differ from the simple past tense? This blog post helps learn past perfect tense with clear rules, structure, and examples. Mastering this tense will improve your ability to describe sequences of past events accurately.
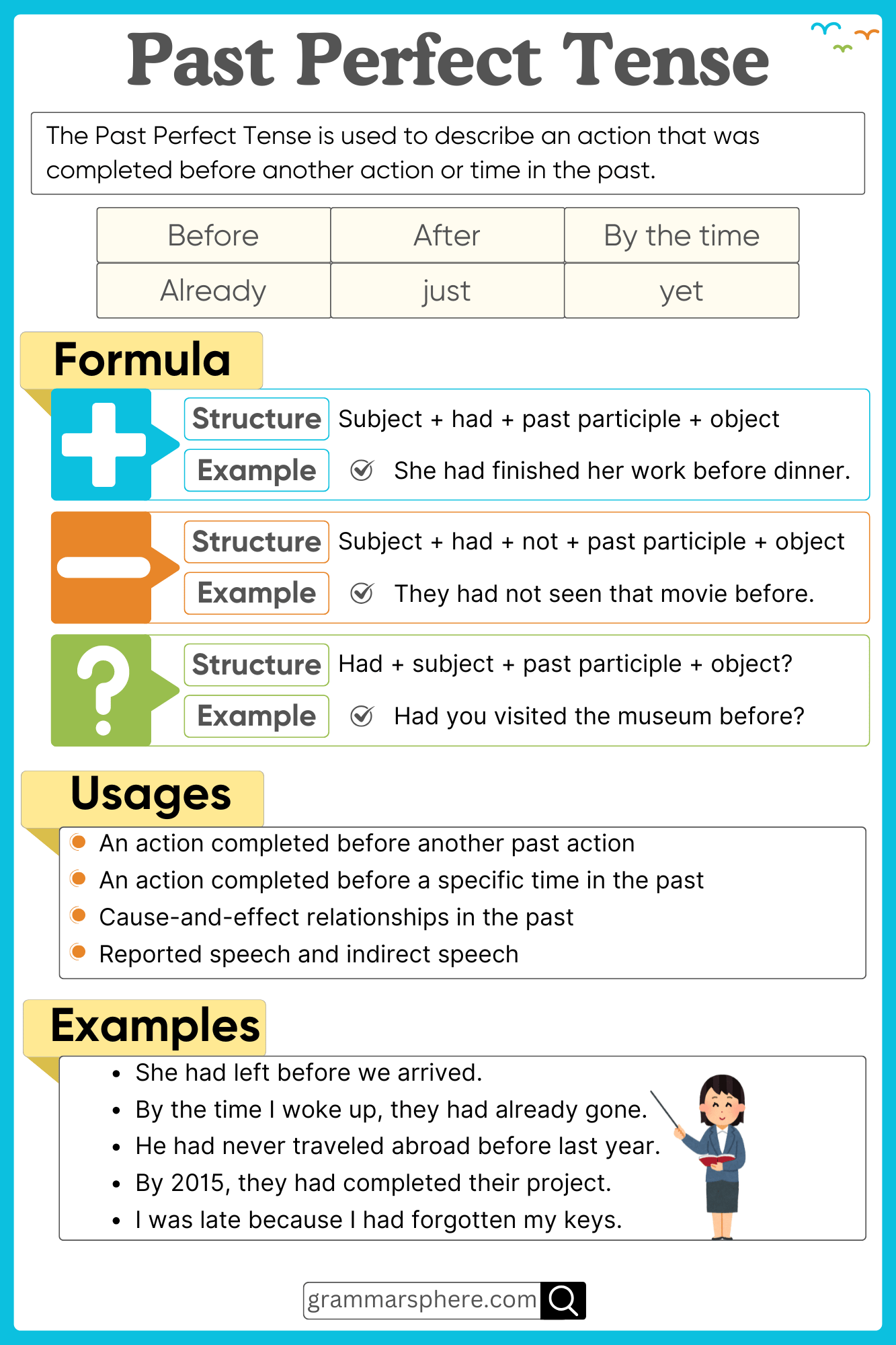
What is Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense describes an action that was completed before another past action or a specific point in the past. It is used to show the sequence of past events clearly.
Structure of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is formed using: Subject + had + past participle (V3) + object
1. Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had + past participle + object
- Aisha had finished her homework before dinner.
- They had left the office when I arrived.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had not + past participle + object
- Aisha had not finished her homework before dinner.
- They had not left the office when I arrived.
3. Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Had + subject + past participle + object?
- Had Aisha finished her homework before dinner?
- Had they left the office when you arrived?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + had + subject + past participle + object?
- Why had Aisha finished her homework so early?
- When had they left the office?
Subject-Verb Agreement
The auxiliary verb had remains the same for all subjects:
| Subject Type | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| I/We/You/They | had |
| He/She/It | had |
Time Expressions in Past Perfect Tense
Time expressions commonly used with this tense include:
- Before: She had left before I arrived.
- After: They had eaten after the guests arrived.
- By the time: By the time we reached, the train had left.
- Already: He had already completed his project before the deadline.
- Just: I had just finished my meal when he called.
Adverb Placement
- Before the main verb: She had always wanted to visit Turkey.
- After the object: They had completed the project successfully.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
1. To Show the Sequence of Past Events
The past perfect tense helps clarify that one event happened before another in the past.
- Ahmed had left before we reached the station.
- The guests had already eaten when we arrived at the party.
2. To Describe a Completed Action Before a Specific Time
When an action is finished before a certain past time, we use the past perfect tense.
- By 10 PM, they had finished their work.
- By the time she turned 18, Aisha had traveled to five countries.
3. To Indicate an Unreal Condition in the Past
In conditional sentences (third conditional), the past perfect tense is used to talk about hypothetical situations that did not happen in the past.
- If he had studied, he would have passed the exam.
- If they had left earlier, they wouldn’t have missed the flight.
4. To Emphasize Duration Before Another Past Action
The past perfect tense is also used to highlight how long an action lasted before another past event occurred.
- She had worked there for five years before she moved to another city.
- They had lived in Istanbul for a decade before they relocated to Dubai.
Past Perfect vs. Past Perfect Continuous
| Tense | Structure | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Past Perfect | Had + Past Participle | Completed action before another past event | Aisha had finished her homework before her friend arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Had been + Verb-ing | Ongoing action before another past event, emphasizes duration | Aisha had been studying for two hours before the exam started. |
Examples of the Past Perfect Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Aisha had packed her bags before the taxi arrived.
- We had locked the doors before leaving the house.
- He had saved enough money before buying a car.
- The guests had left before it started raining.
- I had completed my project before the deadline.
Negative:
- Sara had not seen that movie before yesterday.
- They had not met each other before the event.
- I had not finished my homework before dinner.
- Ahmed had not heard about the new rule.
- We had not visited that place before the trip.
Interrogative:
- Had she cleaned the room before guests arrived?
- Had you ever traveled abroad before this year?
- Had the baby slept before they returned?
- Had he called you before making the decision?
- Had we met before the conference?
Common Mistakes with the Past Perfect Tense
1. Incorrect Use of “Went” Instead of “Gone”
❌ He had went to the market before it rained.
✅ He had gone to the market before it rained.
2. Incorrect Use of “Ate” Instead of “Eaten”
❌ We had ate lunch before noon.
✅ We had eaten lunch before noon.
3. Incorrect Use of “See” Instead of “Seen”
❌ She had see that movie already.
✅ She had seen that movie already.
FAQs
When do we use the Past Perfect Tense?
We use it to show which action happened first in the past.
What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Simple?
Past Perfect shows an earlier action, while Past Simple describes a completed past action.
Can we use “had” with all subjects?
Yes, “had” remains the same for all subjects.
Read More



Leave a Comment