Table of Contents
In this blog post, you will learn about the different types of adverbs in English. Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to give more details about actions, descriptions, or other qualities. Understanding adverbs helps you create more clear and precise sentences. We will cover the main types, such as adverbs of manner, time, place, frequency, and degree, with simple examples to make learning easier.
What is An Adverb?
Example sentences:
She sings beautifully. (How does she sing? Beautifully.)
He arrived late. (When did he arrive? Late.)
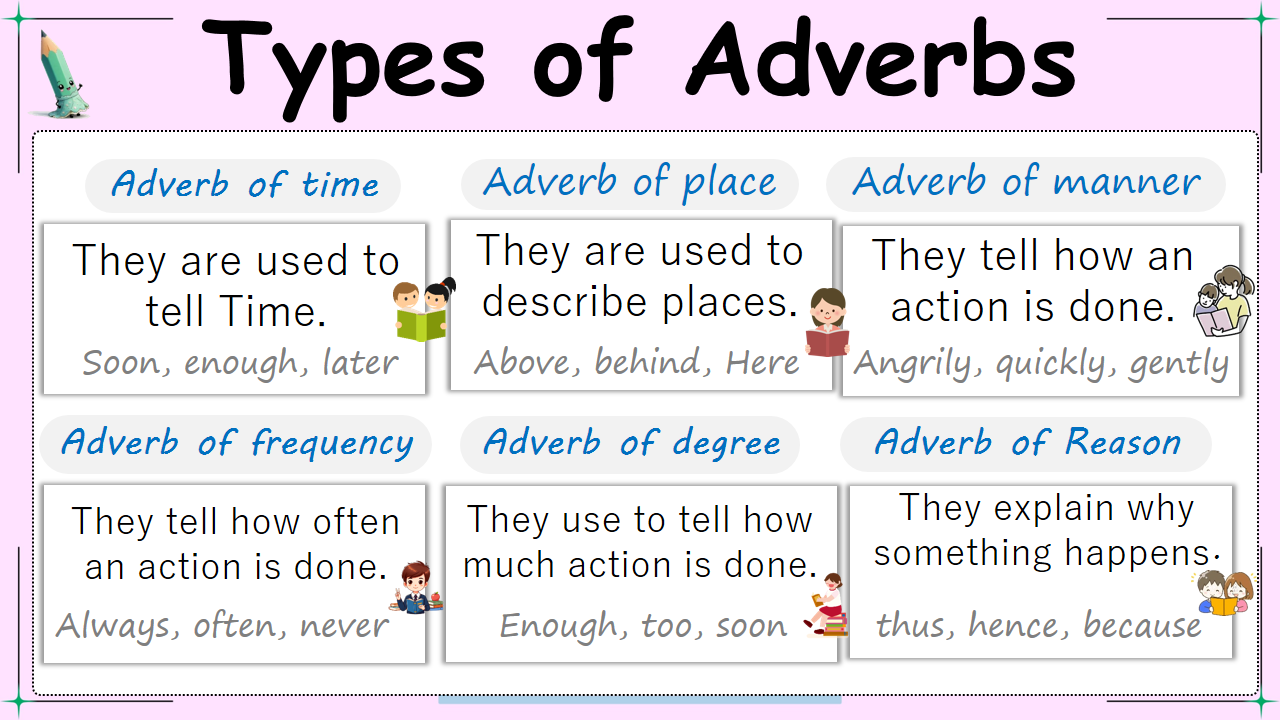
Types of Adverbs
There are several types of adverbs that perform different roles in a sentence. Let’s take a closer look at them:
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Certainty
- Adverbs of Interrogation
- Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
- Adverbs of Reason
1. Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed.
Common Adverbs of Manner: carefully, quickly, beautifully, slowly, easily, skillfully, loudly, quietly, happily, gracefully
Example Sentences:
- She sings beautifully at the concert.
- He drives carefully during rainy weather.
- The cat jumped gracefully onto the table.
- They completed the project quickly.
- She speaks softly so as not to disturb anyone.
2. Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time indicate when an action occurs.
Common Adverbs of Time: today, tomorrow, yesterday, now, soon, later, always, frequently, sometimes, never
Example Sentences:
- He will arrive tomorrow for the meeting.
- We visited them last year during the holidays.
- She is studying now for her exams.
- I usually go to the gym in the evening.
- They rarely eat out on weekdays.
3. Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place show where the action happens.
Common Adverbs of Place: here, there, everywhere, nowhere, outside, inside, above, below, nearby, around
Example Sentences:
- The kids are playing outside in the garden.
- She looked everywhere for her lost ring.
- The book is there on the shelf.
- He sat downstairs while waiting for her.
- I can see my friend nearby.
4. Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency explain how often something happens.
Common Adverbs of Frequency: always, often, frequently, usually, sometimes, rarely, never, occasionally, regularly, seldom
Example Sentences:
- She always reads before bedtime.
- He rarely eats junk food.
- They go to the movies often on weekends.
- I sometimes go for a walk in the evening.
- We never skip breakfast.
5. Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of degree express to what extent something is done.
Common Adverbs of Degree: very, quite, almost, too, extremely, hardly, completely, absolutely, fairly, just
Example Sentences:
- He is very happy with his results.
- She almost finished her homework before dinner.
- The movie was absolutely amazing!
- It’s too hot to go outside today.
- She runs fairly fast for her age.
6. Adverbs of Certainty
Common Adverbs of Certainty: definitely, certainly, surely, probably, undoubtedly, maybe
Example Sentences:
- She will definitely attend the meeting.
- He is probably going to be late.
- They will certainly finish the project on time.
- I will undoubtedly support your decision.
- Maybe we should leave early to avoid traffic.
7. Adverbs of Interrogation
These adverbs are used to ask questions about the manner, time, place, or frequency of an action.
Common Adverbs of Interrogation: how, when, where, why, which, what
Example Sentences:
- How did you learn to play the piano?
- When are you going to the party?
- Where did you put the keys?
- Why are they late?
- What time does the train arrive?
8. Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
Adverbs of affirmation express agreement, while adverbs of negation express disagreement.
Common Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation: yes, indeed, certainly, not, never, no
Example Sentences:
- Yes, I will join you for dinner.
- He is indeed a talented artist.
- She does not like spicy food.
- I have never seen such a beautiful sunset.
- No, I do not agree with that statement.
9. Adverbs of Reason
These adverbs explain why something happens.
Common Adverbs of Reason: therefore, consequently, thus, hence, because
Example Sentences:
- Therefore, we need to reconsider our options.
- She was late; thus, she missed the beginning of the show.
- He didn’t study, consequently, he failed the exam.
- Because it was raining, we stayed indoors.
- Hence, we must act quickly.

Adverb vs. Adverbial Phrase vs. Adverbial Clause
| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or adverb. | She runs quickly. |
| Adverbial Phrase | A group of words acting as an adverb. | She runs in the morning. |
| Adverbial Clause | Has a subject, verb, and conjunction. | She runs because she loves it. |
Example Sentences with Types of Adverbs
Adverbs of Manner
- She sings beautifully at the concert.
- He drives carefully during rainy weather.
- The cat jumped gracefully onto the table.
- They completed the project quickly.
- She speaks softly so as not to disturb anyone.
2. Adverbs of Time
- He will arrive tomorrow for the meeting.
- We visited them last year during the holidays.
- She is studying now for her exams.
- I usually go to the gym in the evening.
- They rarely eat out on weekdays.
3. Adverbs of Place
- The kids are playing outside in the garden.
- She looked everywhere for her lost ring.
- The book is there on the shelf.
- He sat downstairs while waiting for her.
- I can see my friend nearby.
4. Adverbs of Frequency
- She always reads before bedtime.
- He rarely eats junk food.
- They go to the movies often on weekends.
- I sometimes go for a walk in the evening.
- We never skip breakfast.
5. Adverbs of Degree
- He is very happy with his results.
- She almost finished her homework before dinner.
- The movie was absolutely amazing!
- It’s too hot to go outside today.
- She runs extremely fast for her age.
Common Mistakes with Types of Adverbs
1. Confusing Adverbs and Adjectives
✗ She runs good.
✓ She runs well.
2. Overusing Adverbs
Too many adverbs can make writing unclear.
✗ She quickly ran very quickly to the store because she was extremely late.
✓ She sprinted to the store because she was late.
3. Misplacing Adverbs
Adverbs should be placed near the words they modify.
✗ She almost drove her kids to school every day. (Implies she didn’t drive them)
✓ She drove her kids to school almost every day. (Correct placement)
List of Common Adverbs
- Quickly
- Slowly
- Carefully
- Eagerly
- Suddenly
- Often
- Rarely
- Always
- Sometimes
- Never
- Today
- Yesterday
- Tomorrow
- Here
- There
- Everywhere
- Up
- Down
- Very
- Almost
FAQS about Adverb in English
How do I identify an adverb?
How: She sings beautifully.
When: He arrives early.
Where: They live nearby.
To what extent: She runs very fast.
Adverbs often end in -ly, but not always (e.g., fast, well).
What is an adverb and example?
Examples:
She runs quickly. (modifies the verb “runs”)
She speaks very clearly. (modifies the adverb “clearly”)
What is the difference between a verb and an adverb?
Example: She runs fast.
Adverb: An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb, giving more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
Example: She runs quickly.
How to form adverbs?
Examples:
Quick → Quickly
Happy → Happily
Slow → Slowly
You May Also Like




Leave a Comment